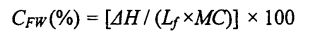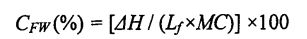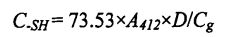Kesan hidroksipropil metilcellulose (HPMC) pada sifat pemprosesan adunan beku dan mekanisme yang berkaitan
Wheat gluten is the material basis for the formation of dough network structure. Experiments found that the addition of I--IPMC reduced the breakage of Yd and disulfide bonds between wheat gluten proteins during frozen storage. Di samping itu, hasil resonans magnetik nuklear rendah dan pengimbasan pembezaan peralihan keadaan air dan fenomena penyambungan semula adalah terhad, dan kandungan air beku dalam doh dikurangkan, dengan itu menekan kesan pertumbuhan kristal ais pada mikrostruktur gluten dan konformasi spatialnya. Pengimbasan mikroskop elektron menunjukkan secara intuitif bahawa penambahan HPMC dapat mengekalkan kestabilan struktur rangkaian gluten.
Starch is the most abundant dry matter in dough, and changes in its structure will directly affect the gelatinization characteristics and the quality of the final product. X. The results of X-ray diffraction and DSC showed that the relative crystallinity of starch increased and the gelatinization enthalpy increased after frozen storage. With the prolongation of frozen storage time, the swelling power of starch without HPMC addition decreased gradually, while the starch gelatinization characteristics (peak viscosity, minimum viscosity, final viscosity, decay value and retrogradation value) all increased significantly; Semasa masa penyimpanan, berbanding dengan kumpulan kawalan, dengan peningkatan penambahan HPMC, perubahan struktur kristal kanji dan sifat gelatinisasi secara beransur -ansur menurun.
Jadual Kandungan
1.1.6 Aplikasi Hydrocolloids dalam Peningkatan Kualiti Doh Frozen .................... .5
1.1.7 Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, I-IPMC) ………. 5
2.2.3 Kaedah Eksperimen .............................................................................................. 9
2.3 Hasil dan Perbincangan Eksperimen ..................................................................... 11
2.3.2 Kesan penambahan HPMC pada sifat -sifat farinaceous doh ....................11
2.3.5 Kesan Jumlah Penambahan HPMC dan Masa Penyimpanan Pembekuan pada Kandungan Air Beku (GW) dalam Doh Frozen ............. ...................................................................................................................
3.2.3 Experimental reagents…………………………………………………………………………. ................. 25
3.2.4 Experimental methods ....................................................................................................... 25
3.3.2 The effect of adding amount of HPMC and freezing storage time on the freezable moisture content (CFW) and thermal stability……………………………………………………………………. 30
3.3.3 Effects of HPMC addition amount and freezing storage time on free sulfhydryl content (C vessel) …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 34
3.3.5 Kesan Jumlah Penambahan HPMC dan Masa Penyimpanan Pembekuan pada Struktur Sekunder Gluten .........................................................................................................................................................................................
3.3.6 Kesan Jumlah Penambahan FIPMC dan Masa Pembekuan pada Permukaan Hidrofobisiti Protein Gluten ...........................................................................................................
Bab 4 Kesan penambahan HPMC pada struktur dan sifat kanji di bawah keadaan penyimpanan beku .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
4.1 Pengenalan ......................................................................................................... 44
4.2 Experimental materials and methods ................................................................................. 45
4.2.1 Bahan Eksperimen ...................................................................................... ............ .45
4.3 Analisis dan Perbincangan ............................................................................................... 48
4.3.1 Content of basic components of wheat starch ……………………………………………………. 48
4.3.3 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing storage time on the shear viscosity of starch paste………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 52
4.3.6 Effects of I-IPMC addition amount and frozen storage time on the thermodynamic properties of starch ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 57
4.4 Ringkasan Bab ............................................................................................... 6 1
Chapter 5 Effects of HPMC addition on yeast survival rate and fermentation activity under frozen storage conditions………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 62
5.1Tan Pengenalan ........................................................................................................... 62
5.2 Materials and methods ............................................................................................................ 62
5.2.1 Bahan dan Instrumen Eksperimen .........................................................................................................................................
5.2.2 Kaedah Eksperimen. . . . . ........................................................................ 63
5.3 Results and Discussion ............................................................................................................... 64
5.3.3 The effect of adding amount of HPMC and freezing time on the content of glutathione in dough……………………………………………………………………………………………………………66. "
5.4 Ringkasan Bab ................................................................................................. 67
6.1 Conclusion ................................................................................................................................. . 68
6.2 Outlook .......................................................................................................................................... 68
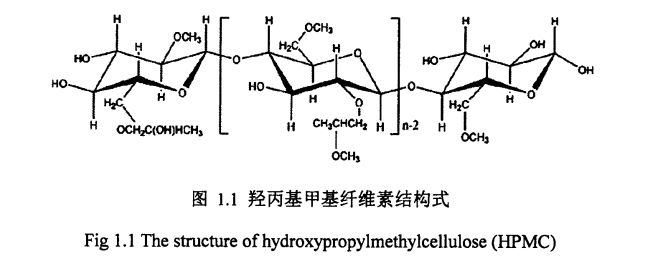
Rajah 1.1 Formula struktur hydroxypropyl methylcellulose ......................... . 6
Rajah 2.2 Kesan penambahan HPMC dan masa pembekuan pada jumlah tertentu roti kukus ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Rajah 2.4 Kesan penambahan HPMC dan masa pembekuan pada keanjalan roti kukus ............................................................................................................................................................................................................... . 20
Figure 3.1 The effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the rheological properties of wet gluten…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 30
Figure 3.2 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing time on the thermodynamic properties of wheat gluten………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 34
Rajah 3.3 Kesan penambahan HPMC dan masa pembekuan pada kandungan sulfhydryl percuma gluten gandum ......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 35
Rajah 3.6 Ilustrasi .................................................................................................... ..........39
Figure 3.7 The effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the microscopic gluten network structure…………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 43
Figure 4.1 Starch gelatinization characteristic curve ............................................................... 51
Figure 4.2 Fluid thixotropy of starch paste ................................................................................. 52
Figure 4.3 Effects of adding amount of MC and freezing time on the viscoelasticity of starch paste……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 57
Figure 4.5 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing storage time on the thermodynamic properties of starch…………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 59
Figure 5.2 The effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the yeast survival rate…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 67
Figure 5.3 Microscopic observation of yeast (microscopic examination) …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 68
Senarai borang
Table 2.1 The basic ingredient content of wheat flour…………………………………………………. 11
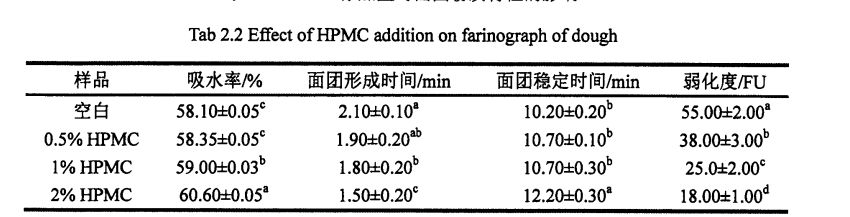
Jadual 2.2 Kesan penambahan i-IPMC pada sifat-sifat farinaceous doh ............... 11
Jadual 2.3 Kesan penambahan i-IPMC pada sifat tegangan doh ......................................14
Jadual 3.1 Kandungan Bahan Asas dalam Gluten ..................................................................25
Table 3.2 Effects of I-IPMC addition amount and freezing storage time on the phase transition enthalpy (Yi IV) and freezer water content (e chat) of wet gluten………………………. 31
Table 3.3 Effects of HPMC addition amount and freezing storage time on the peak temperature (product) of thermal denaturation of wheat gluten…………………………………………. 33
Jadual 3.5 Kesan penambahan HPMC dan masa pembekuan pada struktur sekunder gluten gandum .........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Table 3.6 Effects of I-IPMC addition and freezing storage time on the surface hydrophobicity of wheat gluten……………………………………………………………………………………………. 41
Jadual 4.1 Kandungan komponen asas kanji gandum ................................................... 49
Table 4.3 Effects of I-IPMC addition and freezing time on the shear viscosity of wheat starch paste…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 55
1.1Research Status di rumah dan di luar negara
1.1.1 Pengenalan kepada roti kukus
Steamed bread refers to the food made from the dough after proofing and steaming. As a traditional Chinese pasta food, steamed bread has a long history and is known as "Oriental Bread". Because its finished product is hemispherical or elongated in shape, soft in taste, delicious in taste and rich in nutrients [l], it has been widely popular among the public for a long time. Ia adalah makanan ruji negara kita, terutama penduduk utara. The consumption accounts for about 2/3 of the dietary structure of products in the north, and about 46% of the dietary structure of flour products in the country [21].
1.1.2Search Status Roti Kukus
2)Research on the processing and compounding of special flour for steamed bread. The effect of flour properties on the quality of dough and steamed buns and the research on new special flour for steamed buns, and based on this, an evaluation model of flour processing suitability was established [7]; Sebagai contoh, kesan kaedah penggilingan tepung yang berlainan pada kualiti tepung dan roti kukus [7] 81; Kesan pengkompaunan beberapa tepung gandum waxy pada kualiti roti kukus [9j et al.; Zhu, Huang, &Khan (2001) evaluated the effect of wheat protein on the quality of dough and northern steamed bread, and considered that gliadin/ Glutenin was significantly negatively correlated with dough properties and steamed bread quality [lo]; Zhang, et a1. (2007) analyzed the correlation between gluten protein content, protein type, dough properties and steamed bread quality, and concluded that the content of high molecular weight glutenin subunit (1ligh.molecular-weight, HMW) and total protein content are all related to the quality of northern steamed bread. mempunyai kesan yang signifikan [11].
3) Penyelidikan mengenai penyediaan doh dan teknologi membuat roti kukus. Penyelidikan mengenai pengaruh keadaan proses pengeluaran roti kukus pada pengoptimuman kualiti dan prosesnya; Liu Changhong et al. (2009) showed that in the process of dough conditioning, process parameters such as water addition, dough mixing time, and dough pH value have an impact on the whiteness value of steamed bread. Ia mempunyai kesan yang signifikan terhadap penilaian deria. Sekiranya keadaan proses tidak sesuai, ia akan menyebabkan produk menjadi biru, gelap atau kuning. The research results show that during the dough preparation process, the amount of water added reaches 45%, and the dough mixing time is 5 minutes, ~ When the pH value of the dough was 6.5 for 10 min, the whiteness value and sensory evaluation of the steamed buns measured by the whiteness meter were the best. Apabila menggulung doh 15-20 kali pada masa yang sama, adunannya adalah permukaan yang licin, licin, elastik dan berkilat; when the rolling ratio is 3:1, the dough sheet is shiny, and the whiteness of the steamed bread increases [l to; Li, et a1. (2015) explored the production process of compound fermented dough and its application in steamed bread processing [13].
4)Research on quality improvement of steamed bread. Penyelidikan mengenai penambahan dan penggunaan penambahbaikan kualiti roti yang dikukus; mainly including additives (such as enzymes, emulsifiers, antioxidants, etc.) and other exogenous proteins [14], starch and modified starch [15], etc. The addition and optimization of the corresponding process It is particularly noteworthy that in recent years, through the use of some exogenous proteins and other additives, gluten-free (free. gluten) pasta products have been developed to meet the requirements of celiac disease (Dietary needs of patients with Coeliac Disease [16.1 cit.
6) Penyelidikan mengenai penggunaan bakteria dan masam yang ditapai baru. Jiang, et a1. (2010) Permohonan Chaetomium sp. ditapai untuk menghasilkan xylanase (dengan termostable) dalam roti kukus [2L '; Gerez, et a1. (2012) used two kinds of lactic acid bacteria in fermented flour products and evaluated their quality [221; Wu, et al. (2012) studied the influence of sourdough fermented by four kinds of lactic acid bacteria (Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus, sanfranciscemis , Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp bulgaricus) on the quality (specific volume, texture, fermentation flavor, etc.) of northern steamed bread [23]; dan Gerez, et a1. (2012) used the fermentation characteristics of two kinds of lactic acid bacteria to accelerate the hydrolysis of gliadin to reduce the allergenicity of flour products [24] and other aspects.
7) Penyelidikan mengenai penggunaan doh beku dalam roti kukus.
Among them, steamed bread is prone to aging under conventional storage conditions, which is an important factor restricting the development of steamed bread production and processing industrialization. After aging, the quality of steamed bread is reduced - the texture becomes dry and hard, dregs, shrinks and cracks, the sensory quality and flavor deteriorate, the digestion and absorption rate decreases, and the nutritional value decreases. This not only affects its shelf life, but also creates a lot of waste. According to statistics, the annual loss due to aging is 3% of the output of flour products. 7%. Dengan peningkatan taraf hidup dan kesedaran kesihatan rakyat, serta perkembangan pesat industri makanan, bagaimana untuk memanfaatkan produk mi ruji popular tradisional termasuk roti kukus, dan mendapatkan produk dengan kualiti tinggi, jangka hayat yang panjang dan pemeliharaan yang mudah untuk memenuhi keperluan permintaan yang semakin meningkat untuk makanan yang segar, selamat, berkualiti tinggi dan mudah adalah masalah teknikal yang lama. Based on this background, frozen dough came into being, and its development is still in the ascendant.
b) Kaedah doh pra-bukti dan pembekuan: Doh dibahagikan kepada satu bahagian, satu bahagian dibuktikan, satu adalah cepat beku, satu dibekukan, satu dicairkan, satu dibuktikan dan dimasak (membakar, mengukus, dan lain-lain)
Cakes and other pasta products have different degrees of application [26-27]. Menurut statistik yang tidak lengkap, pada tahun 1990, 80% roti di Amerika Syarikat menggunakan adunan beku; 50% roti di Jepun juga menggunakan adunan beku. twentieth century
Teknologi doh beku sudah pasti memberikan idea yang sesuai untuk pengeluaran industri makanan tradisional Cina seperti roti kukus. However, this processing technology still has some shortcomings, especially under the condition of longer freezing time, the final product will have longer proofing time, lower specific volume, higher hardness, Water loss, poor taste, reduced flavor, and quality deterioration. In addition, due to freezing
Dough is a multi-component (moisture, protein, starch, microorganism, etc.), multi-phase (solid, liquid, gas), multi-scale (macromolecules, small molecules), multi-interface (solid-gas interface, liquid-gas interface), solid-liquid interface) soft material system 1281, so the reasons for the above-mentioned quality deterioration are very complex and pelbagai.
c)Expand, optimize and use new frozen dough quality improvers, which is conducive to the optimization of production enterprises and the innovation and cost control of product types. Pada masa ini, ia masih perlu diperkuat dan diperluaskan lagi;
In view of the above problems and challenges of frozen dough, the long-term innovative research on the application of frozen dough technology, the quality control and improvement of frozen dough products, and the related mechanism of changes in the structure and properties of material components in the frozen dough system and quality deterioration Such research is a hot issue in the field of frozen dough research in recent years. Khususnya, penyelidikan domestik dan asing utama pada tahun -tahun kebelakangan ini terutamanya memberi tumpuan kepada perkara -perkara berikut:
i.Study the changes in the structure and properties of frozen dough with the extension of freezing storage time, in order to explore the reasons for the deterioration of product quality, especially the effect of ice crystallization on biological macromolecules (protein, starch, etc.), for example, ice crystallization. Pembentukan dan pertumbuhan dan hubungannya dengan keadaan air dan pengedaran; changes in wheat gluten protein structure, conformation and properties [31]; perubahan dalam struktur dan sifat kanji; Perubahan dalam mikrostruktur doh dan sifat yang berkaitan, dan sebagainya. 361.
Ii. Pengoptimuman proses pengeluaran doh beku, keadaan penyimpanan beku dan formula. During the production of frozen dough, temperature control, proofing conditions, pre-freezing treatment, freezing rate, freezing conditions, moisture content, gluten protein content, and thawing methods will all affect the processing properties of frozen dough [37]. In general, higher freezing rates produce ice crystals that are smaller in size and more uniformly distributed, while lower freezing rates produce larger ice crystals that are not uniformly distributed. In addition, a lower freezing temperature even below the glass transition temperature (CTA) can effectively maintain its quality, but the cost is higher, and the actual production and cold chain transportation temperatures are usually small. In addition, the fluctuation of the freezing temperature will cause recrystallization, which will affect the quality of the dough.
Iii. Using additives to improve the product quality of frozen dough. In order to improve the product quality of frozen dough, many researchers have made explorations from different perspectives, for example, improving the low temperature tolerance of material components in frozen dough, using additives to maintain the stability of the dough network structure [45.56], etc. Among them, the use of additives is an effective and widely used method. Mainly include, i) enzyme preparations, such as, transglutaminase, O [. Amylase; ii) emulsifiers, such as monoglyceride stearate, DATEM, SSL, CSL, DATEM, etc.; iii) antioxidants, ascorbic acid, etc.; iv) polysaccharide hydrocolloids, such as guar gum, yellow Originalgum, gum Arabic, konjac gum, sodium alginate, etc.; v) other functional substances, such as Xu, et a1. (2009) added Ice-structuring Proteins to wet gluten mass under freezing conditions, and studied its protective effect and mechanism on the structure and function of gluten protein [y71.
Ⅳ. Pembiakan yis antibeku dan penggunaan antibeku ragi baru [58-59]. Sasano, et a1. (2013) obtained freeze-tolerant yeast strains through hybridization and recombination between different strains [60-61], and S11i, Yu, & Lee (2013) studied a biogenic ice nucleating agent derived from Erwinia Herbicans used to protect the fermentation viability of yeast under freezing conditions [62J.
The chemical nature of hydrocolloid is a polysaccharide, which is composed of monosaccharides (glucose, rhamnose, arabinose, mannose, etc.) through 0 [. 1-4. Glycosidic bond or/and a. 1-"6, ikatan glycosidic atau B. 1-4, ikatan glikosid dan 0 [.1-3. polysaccharides, such as konjac gum, guar gum, gum Arabic ; ③ seaweed polysaccharides, such as seaweed gum, carrageenan; ④ microbial polysaccharides, such as Xanthan gum .Polysaccharide has strong hydrophilicity because it contains a large number of hydroxyl groups that are easy to form hydrogen bonds with water, and has Fungsi mengawal penghijrahan, keadaan dan pengedaran air dalam sistem makanan. Digunakan secara meluas untuk dimasukkan ke dalam pemprosesan makanan produk tepung. Wang Xin et al. (2007) studied the effect of adding seaweed polysaccharides and gelatin on the glass transition temperature of dough [631. Wang Yusheng et al. (2013) percaya bahawa penambahan kompaun pelbagai koloid hidrofilik dapat mengubah aliran adunan dengan ketara. Tukar sifat -sifat, tingkatkan kekuatan tegangan adunan, meningkatkan keanjalan doh, tetapi mengurangkan kelanjutan adunan [padam.
Although HPMC has been used in pasta to a certain extent, it is mainly used as an anti-aging agent and water-retaining agent for bread, etc., which can improve product specific volume, texture properties and prolong shelf life [71.74]. However, compared with hydrophilic colloids such as guar gum, xanthan gum, and sodium alginate [75-771], there are not many studies on the application of HPMC in frozen dough, whether it can improve the quality of steamed bread processed from frozen dough. Masih terdapat kekurangan laporan yang berkaitan dengan kesannya.
At present, the application and large-scale production of frozen dough processing technology in my country as a whole is still in the development stage. Pada masa yang sama, terdapat perangkap dan kekurangan tertentu dalam adunan beku itu sendiri. Faktor -faktor yang komprehensif ini pasti menyekat permohonan dan promosi doh beku. on the other hand,this also means that the application of frozen dough has great potential and broad prospects, especially from the perspective of combining frozen dough technology with the industrialized production of traditional Chinese noodles (non-)fermented staple food, to develop more products that meet the needs of Chinese residents. It is of practical significance to improve the quality of the frozen dough based on the characteristics of Chinese pastry and the dietary habits, and is suitable for the processing characteristics of Chinese pastry.
1.3 Kandungan utama kajian
Generally speaking, the material composition of dough used for making fermented flour products mainly includes biological macromolecular substances (starch, protein), inorganic water, and yeast of organisms, and is formed after hydration, cross-linking and interaction. A stable and complex material system with a special structure has been developed. Banyak kajian telah menunjukkan bahawa sifat doh mempunyai kesan yang signifikan terhadap kualiti produk akhir. Therefore, by optimizing the compounding to meet the specific product and it is a research direction to improve the dough formulation and technology of the quality of the product or food for use; on the other hand, improving or improving the properties of dough processing and preservation to ensure or improve the quality of the product is also an important research issue.
Seperti yang dinyatakan dalam pengenalan, menambah HPMC ke sistem doh dan mengkaji kesannya terhadap sifat doh (Farin, pemanjangan, rheologi, dll.) Dan kualiti produk akhir adalah dua kajian yang berkait rapat.
2.2 Bahan dan Kaedah Eksperimen
Zhongyu Gandum tepung Binzhou Zhongyu Food Co., Ltd.; Angel Active Dry Yeast Angel Yeast Co., Ltd.; HPMC (Metil Penggantian Ijazah 28%.30%, Hydroxypropyl Substitation Ijazah 7%.12%) Aladdin (Shanghai) syarikat reagen kimia; all chemical reagents used in this experiment are of analytical grade;
BPS. Kotak malar dan kelembapan 500CL
Keseimbangan analisis elektronik BSAL24S
DHG. Ketuhar pengeringan letupan 9070A
Sm. 986s Dough Mixer
C21. KT2134 POOKER INDUCTION
Meter serbuk. E
Extensometer. E
Q200 Calorimeter Pengimbasan Berbeza
FD. 1b. 50 pengering pembekuan vakum
Kjelte TM 8400 Kjeldahl Nitrogen Analyzer automatik
Pengilang
Sartorius, Jerman
American TA Company
American TA Company
2.2.3.1 Penentuan Komponen Asas Tepung
2.2.3.2 Penentuan sifat -sifat Floury
2.2.3.3 Penentuan sifat tegangan adunan
Penentuan sifat tegangan adunan mengikut GB/T 14615.2006 [831.
2.2.3.4 Pengeluaran adunan beku
Timbang sampel kira -kira 15 mg bahagian tengah adunan yang cair sepenuhnya, tutupkannya dalam aluminium crucible (sesuai untuk sampel cecair), dan mengukurnya dengan kalorimetri pengimbasan pembezaan (DSC). The specific program parameters are set. As follows: first equilibrate at 20°C for 5 min, then drop to .30°C at a rate of 10"C/min, keep for 10 min, and finally rise to 25°C at a rate of 5"C/min, the purge gas is nitrogen (N2) And its flow rate was 50 mL/min. Menggunakan aluminium kosong yang boleh dibuang sebagai rujukan, lengkung DSC yang diperoleh dianalisis menggunakan perisian analisis Analisis Universal 2000, dan entalpi lebur (hari) kristal ais diperoleh dengan mengintegrasikan puncak yang terletak pada kira -kira 0 ° C. Freezable water content (CFW) is calculated by the following formula [85.86]:
Antaranya, 厶 mewakili haba laten kelembapan, dan nilainya ialah 334 J Dan; MC (total Moisture Content) represents the total moisture content in the dough (measured according to GB 50093.2010t78]). Each sample was repeated three times.
2.2.3.8 Penilaian Kualiti Roti Kukus
As shown in Table 2.2, with the increase of HPMC addition, the water absorption of dough increased significantly, from 58.10% (without adding HPMC dough) to 60.60% (adding 2% HPMC dough). Di samping itu, penambahan HPMC meningkatkan masa kestabilan doh dari 10.2 min (kosong) hingga 12.2 min (tambah 2% HPMC). However, with the increase of HPMC addition, both the dough forming time and the dough weakening degree decreased significantly, from the blank dough forming time of 2.10 min and the weakening degree of 55.0 FU, respectively, to the addition of 2% HPMC, the dough forming time was 1. .50 min and weakening degree of 18.0 FU, decreased by 28.57% and 67.27%, respectively.
Table 2.3 lists the effects of different amounts of HPMC (O, 0.5%, 1% and 2%) and different proofing 1'9 (45 min, 90 min and 135 min) on the dough tensile properties (energy, stretch resistance, maximum stretch resistance, elongation, stretch ratio and maximum stretch ratio). The experimental results show that the tensile properties of all dough samples increase with the extension of the proofing time except the elongation which decreases with the extension of the proofing time. Untuk nilai tenaga, dari 0 hingga 90 min, nilai tenaga sampel doh yang lain meningkat secara beransur -ansur kecuali penambahan 1% HPMC, dan nilai tenaga semua sampel doh meningkat secara beransur -ansur. There were no significant changes. Ini menunjukkan bahawa apabila masa pemeriksaan adalah 90 min, struktur rangkaian doh (silang silang antara rantai molekul) sepenuhnya terbentuk. Therefore, the proofing time is further extended, and there is no significant difference in the energy value. At the same time, this can also provide a reference for determining the proofing time of the dough. Apabila masa pemeriksaan memanjangkan, lebih banyak ikatan sekunder antara rantai molekul terbentuk dan rantai molekul lebih rapat dengan silang, jadi rintangan tegangan dan rintangan tegangan maksimum meningkat secara beransur-ansur. Pada masa yang sama, kadar ubah bentuk rantaian molekul juga berkurangan dengan peningkatan ikatan sekunder antara rantai molekul dan penyambungan silang rentetan rantaian molekul, yang menyebabkan penurunan pemanjangan doh dengan lanjutan masa yang berlebihan. The increase in tensile resistance/maximum tensile resistance and the decrease in elongation resulted in an increase in tensile LL/maximum tensile ratio.
Walau bagaimanapun, penambahan HPMC dapat menindas trend di atas dan mengubah sifat tegangan adunan. Dengan peningkatan penambahan HPMC, rintangan tegangan, rintangan tegangan maksimum dan nilai tenaga doh semua menurun bersamaan, sementara pemanjangan meningkat. Specifically, when the proofing time was 45 min, with the increase of HPMC addition, the dough energy value decreased significantly, from 148.20-J: 5.80 J (blank) to 129.70-J respectively: 6.65 J (add 0.5% HPMC), 120.30 ± 8.84 J (add 1% HPMC), and 110.20-a: 6.58
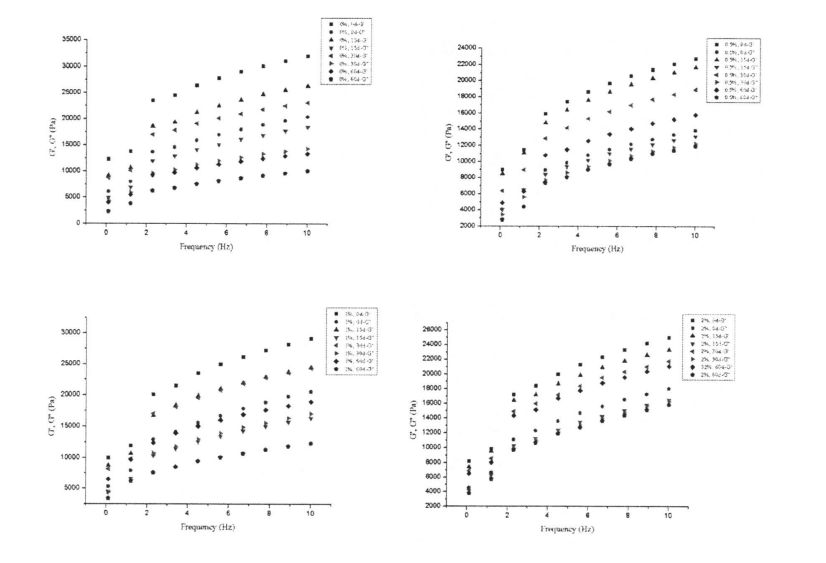
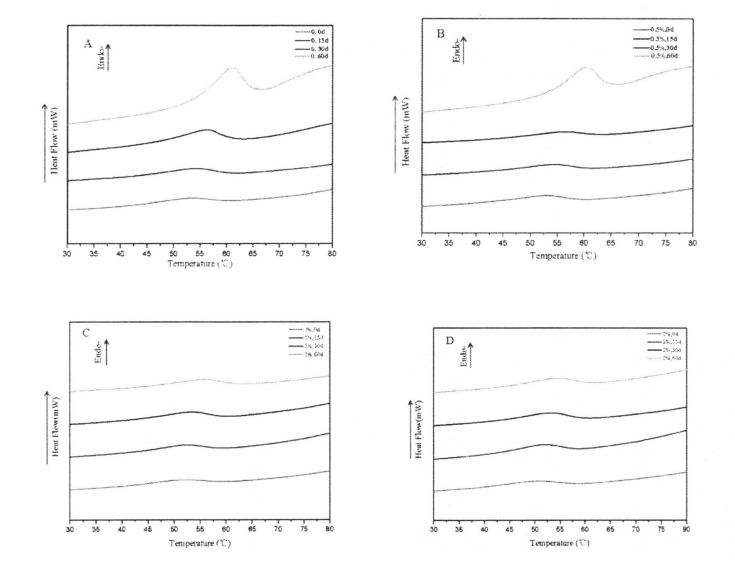
Figure 2.1 shows the change of storage modulus (elastic modulus, G') and loss modulus (viscous modulus, G") of dough with different HPMC content from 0 days to 60 days. The results showed that with the prolongation of freezing storage time, the G' of the dough without adding HPMC decreased significantly, while the change of G" was relatively small, and the /an Q (G''/G') increased. This may be due to the fact that the network structure of the dough is damaged by ice crystals during freezing storage, which reduces its structural strength and thus the elastic modulus decreases significantly. Walau bagaimanapun, dengan peningkatan penambahan HPMC, variasi G 'secara beransur -ansur menurun. In particular, when the added amount of HPMC was 2%, the variation of G' was the smallest. This shows that HPMC can effectively inhibit the formation of ice crystals and the increase in the size of ice crystals, thereby reducing the damage to the dough structure and maintaining the structural strength of the dough. Di samping itu, nilai adunan g lebih besar daripada adunan gluten basah, manakala nilai g "doh lebih kecil daripada adunan gluten basah, terutamanya kerana doh mengandungi sejumlah besar kanji, yang boleh diserap dan disebarkan pada struktur rangkaian gluten.
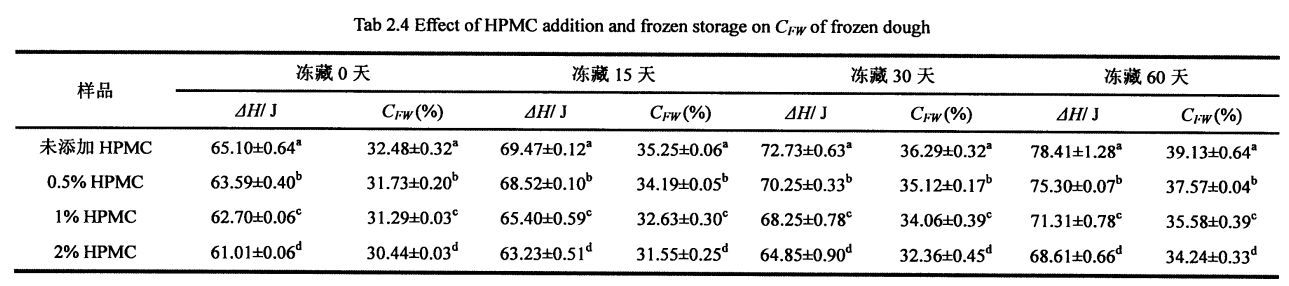
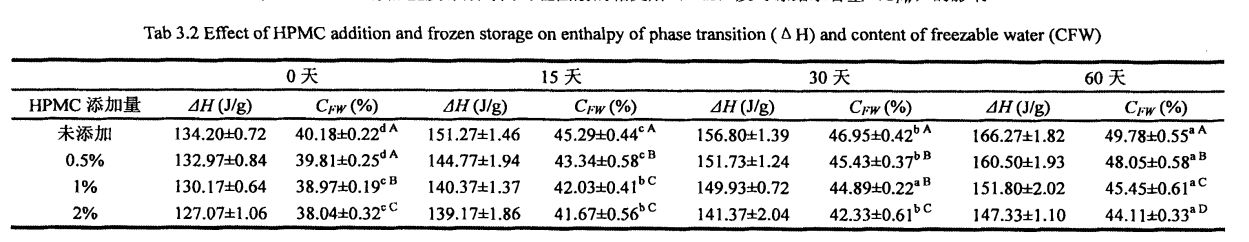
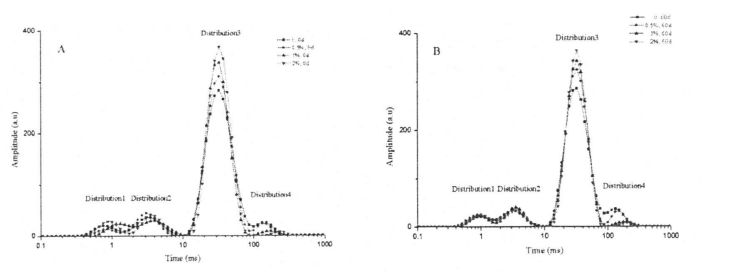
Tidak semua kelembapan dalam adunan boleh membentuk kristal ais pada suhu rendah tertentu, yang berkaitan dengan keadaan kelembapan (aliran bebas, terhad, digabungkan dengan bahan lain, dll.) Dan persekitarannya. Air beku adalah air di dalam adunan yang boleh menjalani transformasi fasa untuk membentuk kristal ais pada suhu rendah. The amount of freezable water directly affects the number, size and distribution of ice crystal formation. In addition, the freezable water content is also affected by environmental changes, such as the extension of freezing storage time, the fluctuation of freezing storage temperature, and the change of material system structure and properties. Untuk adunan beku tanpa menambah HPMC, dengan pemanjangan masa penyimpanan pembekuan, q silikon meningkat dengan ketara, dari 32.48 ± 0.32% (penyimpanan beku selama 0 hari) hingga 39.13 ± 0.64% (penyimpanan beku selama 0 hari). Tibetan for 60 days), the increase rate was 20.47%. Walau bagaimanapun, selepas 60 hari penyimpanan beku, dengan peningkatan penambahan HPMC, kadar kenaikan CFW menurun, diikuti oleh 18.41%, 13.71%, dan 12.48%(Jadual 2.4). Pada masa yang sama, O∥ doh yang tidak berkurangan menurun bersamaan dengan peningkatan jumlah HPMC yang ditambah, dari 32.48A-0.32% (tanpa menambah HPMC) kepada 31.73 ± 0.20% pada gilirannya. (Menambah0.5% HPMC), 3 1.29+0.03% (menambah 1% HPMC) dan 30.44 ± 0.03% (menambah 2% HPMC) kapasiti pegangan air, menghalang aliran air bebas dan mengurangkan jumlah air yang boleh dibekukan. Dalam proses penyimpanan pembekuan, bersama-sama dengan penghabluran semula, struktur doh dimusnahkan, sehingga sebahagian dari air yang tidak dapat dibekukan ditukar menjadi air beku, sehingga meningkatkan kandungan air beku. Walau bagaimanapun, HPMC dapat menghalang pembentukan dan pertumbuhan kristal ais dan melindungi kestabilan struktur doh, dengan itu dengan berkesan menghalang peningkatan kandungan air beku. Ini selaras dengan undang -undang perubahan kandungan air beku dalam adunan gluten basah beku, tetapi kerana doh mengandungi lebih banyak kanji, nilai CFW lebih kecil daripada nilai G∥ yang ditentukan oleh adunan gluten basah (Jadual 3.2).
2.3.6.1 Pengaruh jumlah tambahan HPMC dan masa penyimpanan beku pada jumlah tertentu roti kukus
The specific volume of steamed bread can better reflect the appearance and sensory quality of steamed bread. Semakin besar jumlah spesifik roti kukus, semakin besar jumlah roti kukus yang kualiti yang sama, dan jumlah tertentu mempunyai pengaruh tertentu pada penampilan, warna, tekstur, dan penilaian deria makanan. Generally speaking, steamed buns with larger specific volume are also more popular with consumers to a certain extent.
The specific volume of steamed bread can better reflect the appearance and sensory quality of steamed bread. Semakin besar jumlah spesifik roti kukus, semakin besar jumlah roti kukus yang kualiti yang sama, dan jumlah tertentu mempunyai pengaruh tertentu pada penampilan, warna, tekstur, dan penilaian deria makanan. Generally speaking, steamed buns with larger specific volume are also more popular with consumers to a certain extent.
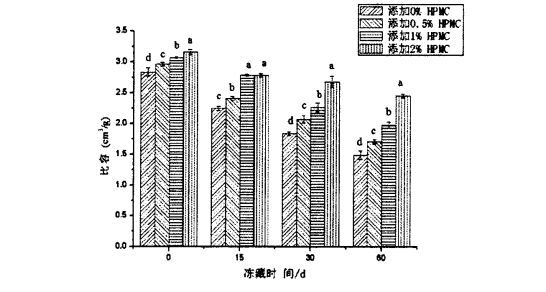
However, the specific volume of the steamed bread made from frozen dough decreased with the extension of the frozen storage time. Antaranya, jumlah spesifik roti kukus yang dibuat dari adunan beku tanpa menambah HPMC adalah 2.835 ± 0.064 cm3/g (penyimpanan beku). 0 days) down to 1.495±0.070 cm3/g (frozen storage for 60 days); while the specific volume of steamed bread made from frozen dough added with 2% HPMC dropped from 3.160±0.041 cm3/g to 2.160±0.041 cm3/g. 451 ± 0.033 cm3/g, oleh itu, jumlah spesifik roti kukus yang diperbuat daripada adunan beku yang ditambah dengan HPMC menurun dengan peningkatan jumlah tambahan. Oleh kerana jumlah spesifik roti kukus bukan sahaja dipengaruhi oleh aktiviti penapaian yis (pengeluaran gas penapaian), kapasiti pemegangan gas sederhana bagi struktur rangkaian doh juga mempunyai kesan penting terhadap jumlah tertentu produk akhir [96'9 yang disebutkan. The measurement results of the above rheological properties show that the integrity and structural strength of the dough network structure are destroyed during the freezing storage process, and the degree of damage is intensified with the extension of the freezing storage time. During the process, its gas holding capacity is poor, which in turn leads to a decrease in the specific volume of the steamed bread. Walau bagaimanapun, penambahan HPMC lebih berkesan melindungi integriti struktur rangkaian doh, supaya sifat-sifat pemegangan udara doh lebih baik dikekalkan, oleh itu, dalam O. semasa tempoh penyimpanan beku selama 60 hari, dengan peningkatan penambahan HPMC, jumlah spesifik roti kukus yang sepadan menurun secara beransur-ansur.
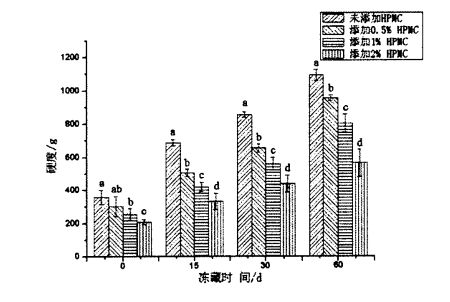
Sebaliknya, dengan pemanjangan masa penyimpanan beku doh beku, kekerasan roti kukus yang dibuat olehnya meningkat dengan ketara (p <0.05), sementara keanjalan menurun dengan ketara (p <0.05). However, the hardness of steamed buns made from frozen dough without added HPMC increased from 358.267 ± 42.103 g (frozen storage for 0 days) to 1092.014 ± 34.254 g (frozen storage for 60 days);
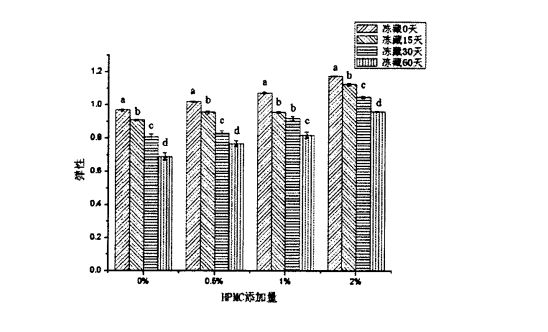
Kekerasan roti kukus yang diperbuat daripada adunan beku dengan 2% HPMC meningkat dari 208.233 ± 15.566 g (penyimpanan beku selama 0 hari) hingga 564.978 ± 82.849 g (penyimpanan beku selama 60 hari). Rajah 2 .4 Kesan penambahan HPMC dan penyimpanan beku pada kepuasan roti kukus Cina dari segi keanjalan, keanjalan roti kukus yang diperbuat daripada adunan beku tanpa menambah HPMC menurun dari 0.968 ± 0.006 (pembekuan selama 0 hari) hingga 0.689 ± 0.022 (beku selama 60 hari); Frozen with 2% HPMC added the elasticity of the steamed buns made of dough decreased from 1.176 ± 0.003 (freezing for 0 days) to 0.962 ± 0.003 (freezing for 60 days). Jelas sekali, kadar peningkatan kekerasan dan kadar pengurangan keanjalan menurun dengan peningkatan jumlah tambahan HPMC dalam adunan beku semasa tempoh penyimpanan beku. Ini menunjukkan bahawa penambahan HPMC dapat meningkatkan kualiti roti kukus. In addition, Table 2.5 lists the effects of HPMC addition and frozen storage time on other texture indexes of steamed bread. ) had no significant change (P>0.05); Walau bagaimanapun, pada 0 hari pembekuan, dengan peningkatan penambahan HPMC, kelembutan dan kekoksatan menurun dengan ketara (p
On the other hand, with the prolongation of freezing time, the cohesion and restoring force of steamed bread decreased significantly. Untuk roti kukus yang diperbuat daripada adunan beku tanpa menambah HPMC, perpaduannya meningkat dengan O. 86-4-0.03 g (penyimpanan beku 0 hari) dikurangkan kepada 0.49+0.06 g (penyimpanan beku selama 60 hari) Walau bagaimanapun, untuk roti kukus yang diperbuat daripada adunan beku dengan 2% HPMC ditambah, perpaduan dikurangkan dari 0.93+0.02 g (0 hari beku) hingga 0.61+0.07 g (penyimpanan beku selama 60 hari) In addition, with the prolongation of frozen storage time, the stickiness and chewiness of steamed bread increased significantly. For the steamed bread made from frozen dough without adding HPMC, the stickiness was increased by 336.54+37. 24 (0 days of frozen storage) increased to 1232.86±67.67 (60 days of frozen storage), while chewiness increased from 325.76+34.64 (0 days of frozen storage) to 1005.83+83.95 (frozen for 60 days); however, for the steamed buns made from frozen dough with 2% HPMC added, the stickiness increased from 206.62+1 1.84 (frozen for 0 days) to 472.84. 96+45.58 (frozen storage for 60 days), while chewiness increased from 200.78+10.21 (frozen storage for 0 days) to 404.53+31.26 (frozen storage for 60 days). Ini menunjukkan bahawa penambahan HPMC dapat menghalang perubahan dalam sifat tekstur roti kukus yang disebabkan oleh penyimpanan pembekuan. In addition, the changes in the texture properties of steamed bread caused by freezing storage (such as the increase of stickiness and chewiness and the decrease of recovery force) There is also a certain internal correlation with the change of steamed bread specific volume. Thus, dough properties (eg, farinality, elongation, and rheological properties) can be improved by adding HPMC to frozen dough, and HPMC inhibits the formation, growth, and redistribution of ice crystals (recrystallization process), making frozen dough The quality of the processed steamed buns is improved.
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is a kind of hydrophilic colloid, and its application research in frozen dough with Chinese-style pasta food (such as steamed bread) as the final product is still lacking. The main purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of HPMC improvement by investigating the effect of HPMC addition on the processing properties of frozen dough and the quality of steamed bread, so as to provide some theoretical support for the application of HPMC in steamed bread and other Chinese-style flour products. Keputusan menunjukkan bahawa HPMC dapat meningkatkan sifat -sifat farinaceous doh. Apabila jumlah tambahan HPMC adalah 2%, kadar penyerapan air doh meningkat daripada 58.10%dalam kumpulan kawalan kepada 60.60%; 2 minit meningkat kepada 12.2 min; at the same time, the dough formation time decreased from 2.1 min in the control group to 1.5 mill; the weakening degree decreased from 55 FU in the control group to 18 FU. In addition, HPMC also improved the tensile properties of the dough. With the increase in the amount of HPMC added, the elongation of the dough increased significantly; significantly reduced. In addition, during the frozen storage period, the addition of HPMC reduced the increase rate of the freezable water content in the dough, thereby inhibiting the damage to the dough network structure caused by ice crystallization, maintaining the relative stability of the dough viscoelasticity and the integrity of the network structure, thereby improving the stability of the dough network structure. The quality of the final product is guaranteed.
On the other hand, the experimental results showed that the addition of HPMC also had a good quality control and improvement effect on steamed bread made from frozen dough. For the unfrozen samples, the addition of HPMC increased the specific volume of the steamed bread and improved the texture properties of the steamed bread - reduced the hardness of the steamed bread, increased its elasticity, and at the same time reduced the stickiness and chewiness of the steamed bread. Di samping itu, penambahan HPMC menghalang kemerosotan kualiti roti kukus yang diperbuat daripada adunan beku dengan lanjutan masa penyimpanan pembekuan - mengurangkan tahap peningkatan kekerasan, keletihan dan kebodohan roti yang dikukus, serta mengurangkan keanjalan roti kukus, kohsian dan pemulihan daya pemulihan.
Gluten gandum adalah protein penyimpanan yang paling banyak dalam bijirin gandum, menyumbang lebih daripada 80% daripada jumlah protein. According to the solubility of its components, it can be roughly divided into glutenin (soluble in alkaline solution) and gliadin (soluble in alkaline solution). dalam penyelesaian etanol). Among them, the molecular weight (mw) of glutenin is as high as 1x107Da, and it has two subunits, which can form intermolecular and intramolecular disulfide bonds; while the molecular weight of gliadin is only 1x104Da, and there is only one subunit, which can form molecules Internal disulfide bond [100]. Campos, Steffe, & Ng (1 996) membahagikan pembentukan doh ke dalam dua proses: input tenaga (proses pencampuran dengan doh) dan persatuan protein (pembentukan struktur rangkaian doh). It is generally believed that during dough formation, glutenin determines the elasticity and structural strength of the dough, while gliadin determines the viscosity and fluidity of the dough [102]. Ia dapat dilihat bahawa protein gluten mempunyai peranan yang sangat diperlukan dan unik dalam pembentukan struktur rangkaian doh, dan memberikan doh dengan perpaduan, viskoelasticity dan penyerapan air.
In addition, from a microscopic point of view, the formation of the three-dimensional network structure of dough is accompanied by the formation of intermolecular and intramolecular covalent bonds (such as disulfide bonds) and non-covalent bonds (such as hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic forces) [103]. Walaupun tenaga ikatan sekunder
Untuk adunan beku, di bawah keadaan pembekuan, pembentukan dan pertumbuhan kristal ais (penghabluran dan proses penghabluran semula) akan menyebabkan struktur rangkaian doh menjadi diperah secara fizikal, dan integriti strukturnya akan dimusnahkan, dan mikroskopik. Accompanied by changes in the structure and properties of gluten protein [105'1061. As Zhao, et a1. (2012) mendapati bahawa dengan pemanjangan masa pembekuan, berat molekul dan radius gyrasi molekul protein gluten menurun [107J, yang menunjukkan bahawa protein gluten sebahagiannya depolimerisasi. Di samping itu, perubahan konformasi spatial dan sifat termodinamik protein gluten akan menjejaskan sifat pemprosesan doh dan kualiti produk. Oleh itu, dalam proses penyimpanan pembekuan, ia adalah kepentingan penyelidikan tertentu untuk menyiasat perubahan keadaan air (keadaan kristal ais) dan struktur dan sifat protein gluten di bawah keadaan masa penyimpanan pembekuan yang berbeza.
Gluten Anhui Rui Fu Xiang Food Co., Ltd.; Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC, same as above) Aladdin Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.
Nama peralatan
Penemuan. R3 rheometer
DSC. Q200 Calorimeter Pengimbasan Berbeza
JSM. 6490LV tungsten filamen pengimbasan mikroskop elektron
FD. 1b. 50 pengering pembekuan vakum
Thermo Fisher FC Penuh Panjang Pengimbasan Mikrofon Pengimbasan
Pb. Model 10 Meter pH
Myp ll. Type 2 Magnetic Stirrer
Mx. S Jenis eddy eddy semasa
Pengilang
American TA Company
American TA Company
Shanghai Niumet Company
Jintan Jincheng Guosheng Kilang Instrumen Eksperimen
Qingdao Haier Group
Hefei Mei Ling Co., Ltd.
Sartorius, Jerman
Thermo Fisher, Amerika Syarikat
Anhui Zhong Ke Zhong Jia Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.
Thermo Fisher, Amerika Syarikat
Scilogex, Amerika Syarikat
3.2.4 Kaedah Eksperimen
3.2.4.1 Penentuan Komponen Asas Gluten
3.2.4.2 Penyediaan adunan gluten basah (adunan gluten)
3.2.4.3 Penentuan sifat rheologi jisim gluten basah
Apabila masa pembekuan yang sama berakhir, ambil jisim gluten basah beku dan letakkan di dalam peti sejuk 4 ° C untuk menyeimbangkan selama 8 jam. Kemudian, ambil sampel dan letakkan pada suhu bilik sehingga sampel sepenuhnya dicairkan (kaedah ini mencairkan jisim gluten basah juga boleh digunakan untuk bahagian eksperimen, 2.7.1 dan 2.9). Sampel (kira -kira 2 g) kawasan pusat jisim gluten basah cair dipotong dan diletakkan pada pembawa sampel (plat bawah) rheometer (Discovery R3). Sapu ketegangan) Untuk menentukan rantau viskoelasticity linear (LVR), parameter eksperimen tertentu ditetapkan seperti berikut - perlawanan adalah plat selari dengan diameter 40 kilang, jurang ditetapkan kepada 1000 MRN, dan suhu ditetapkan kepada 25 ° C, julat pengimbasan strain adalah 0.01%. 100%, the frequency is set to 1 Hz. Then, after changing the sample, let it stand for 10 minutes, and then perform dynamic
Sapu kekerapan, parameter eksperimen tertentu ditetapkan seperti berikut - ketegangan adalah 0.5% (pada LVR), dan julat sapuan frekuensi ialah 0.1 Hz. 10 Hz, while other parameters are the same as the strain sweep parameters. Scanning data is acquired in logarithmic mode, and 5 data points (plots) are recorded in the rheological curve for every 10-fold increase in frequency, so as to obtain the frequency as the abscissa, the storage modulus (G') and the loss modulus (G') is the rheological discrete curve of the ordinate. It is worth noting that after each time the sample is pressed by the clamp, the excess sample needs to be gently scraped with a blade, and a layer of paraffin oil is applied to the edge of the sample to prevent moisture during the experiment. of loss. Each sample was replicated three times.
(1) Penentuan kandungan air beku (silikon CF) dalam jisim gluten basah
Sampel 15 mg gluten basah ditimbang dan dimeteraikan dalam aluminium crucible (sesuai untuk sampel cecair). The determination procedure and parameters are as follows: equilibrate at 20°C for 5 min, then drop to .30°C at a rate of 10°C/min, keep the temperature for 10 min, and finally increase to 25°C at a rate of 5°C/min, purge the gas (Purge Gas) was nitrogen (N2) and its flow rate was 50 mL/min, and a blank sealed aluminum crucible was used as a reference. The obtained DSC curve was analyzed using the analysis software Universal Analysis 2000, by analyzing the peaks located around 0 °C. Integral to get the melting enthalpy of ice crystals (Yu day). Then, the freezable water content (CFW) is calculated by the following formula [85-86]:
Antaranya, tiga, mewakili haba laten kelembapan, dan nilainya ialah 334 J/g; MC represents the total moisture content of the wet gluten measured (measured according to GB 50093.2010 [. 78]). Each sample was replicated three times.
(2) Penentuan suhu puncak denaturasi haba (TP) protein gluten gandum
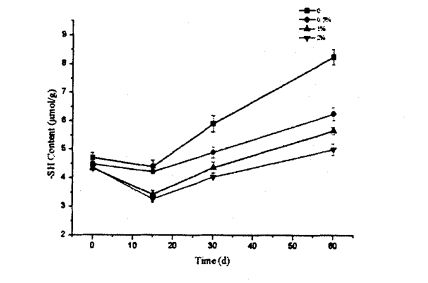
The content of free sulfhydryl groups was determined according to the method of Beveridg, Toma, & Nakai (1974) [Hu], with appropriate modifications. Timbang 40 mg sampel protein gluten gandum, goncang dengan baik, dan membuatnya tersebar dalam 4 ml dodecyl sulfonate
Sodium Sodium (SDS). Tris-hydroxymethyl aminomethane (Tris). Glycine (Gly). Tetraacetic acid 7, amine (EDTA) buffer (10.4% Tris, 6.9 g glycine and 1.2 g EDTA/L, pH 8.0, abbreviated as TGE, and then 2.5% SDS It was added to the above TGE solution (that is, prepared into SDS-TGE buffer), incubated at 25°C for 30 min, and shaken every 10 min. Then, the supernatant was obtained after centrifugation for 10 min at 4°C and 5000×g. First, the protein content in the supernatant was determined by the Coomassie brilliant blue (G.250) method. Then, to the supernatant was added O. 04 mL of Ellman's reagent (dissolve 5,5'. Dithio-2. Nitrobenzoic acid, DTNB at TGE to measure the solution, 4 Rag/ml), selepas 30 minit pengeraman dalam mandi air 25 ℃, tambah penyerapan 412 nm, dan penampan di atas digunakan sebagai kawalan kosong.
In this experiment, a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer equipped with an attenuated single reflection attenuated total reflection (ATR) accessory was used to determine the secondary structure of gluten protein, and a cadmium mercury telluride crystal was used as the detector. Both sample and background collection were scanned 64 times with a resolution of 4 cm~ and a scanning range of 4000 cmq-500 cm~. Sebarkan sedikit serbuk pepejal protein pada permukaan berlian pada pemasangan ATR, dan kemudian, selepas 3 bertukar mengikut arah jam, anda boleh mula mengumpul isyarat spektrum inframerah sampel, dan akhirnya mendapatkan gelombang (wavenumber, cm-1) sebagai abscissa, dan penyerapan sebagai abscissa. (Absorption) is the infrared spectrum of the ordinate.
Menyerap 40 larutan ans (15.0 mmol/l) telah ditambah kepada setiap penyelesaian sampel kecerunan (4 ml), digoncang dan digegarkan dengan baik, kemudian dengan cepat berpindah ke tempat yang terlindung, dan 200 "L tetes cahaya ditarik dari tiub sampel dengan kepekatan yang rendah ke kepekatan yang tinggi. NM sebagai cahaya pengujaan dan 484 pagi sebagai cahaya pelepasan.
3.2.4.9 Pemerhatian Mikroskop Elektron
All results are expressed as mean 4-standard deviation, and the above experiments were repeated at least three times except for scanning electron microscopy. Gunakan asal 8.0 untuk menarik carta, dan gunakan SPSS 19.0 untuk satu. Analisis cara varians dan ujian pelbagai pelbagai Duncan, tahap penting ialah 0.05.
3. Hasil dan perbincangan
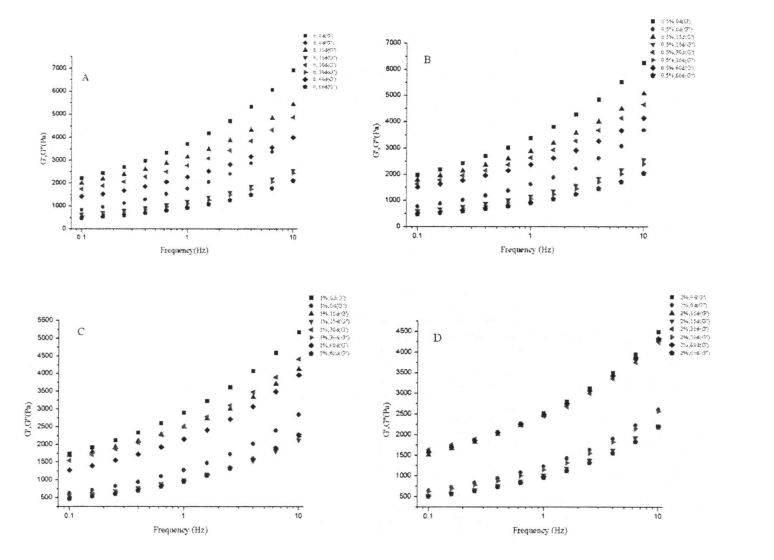
3.3.1 Kesan Jumlah Penambahan HPMC dan Masa Penyimpanan Pembekuan pada Sifat Rheologi Massa Gluten Basah
Ice crystals are formed by the phase transition of freezable water at temperatures below its freezing point. Therefore, the content of freezable water directly affects the number, size and distribution of ice crystals in the frozen dough. The experimental results (Table 3.2) show that as the freezing storage time is extended from 0 days to 60 days, the wet gluten mass Chinese silicon gradually becomes larger, which is consistent with the research results of others [117'11 81]. Khususnya, selepas 60 hari penyimpanan beku, enthalpi peralihan fasa (hari) jisim gluten basah tanpa HPMC meningkat daripada 134.20 j/g (0 d) hingga 166.27 j/g (60 d) Walau bagaimanapun, bagi sampel yang ditambah dengan 0.5%, 1% dan 2% HPMC, selepas 60 hari pembekuan, C-CHAT meningkat sebanyak 20.07%, 16, 63% dan 15.96%, yang konsisten dengan Matuda, et a1. (2008) found that the melting enthalpy (Y) of the samples with added hydrophilic colloids decreased compared with the blank samples [119].
Rajah 3.4 Kesan penambahan FIPMC dan penyimpanan beku pada lengkung pengagihan masa relaksasi melintang untuk adunan gluten
In addition, the height and area of the T24 distribution of the wet gluten mass with different contents of HPMC were significantly different (Fig. 3.4, A), and the relative content of free water was negatively correlated with the amount of HPMC added. This is just the opposite of the Dang distribution. Therefore, this variation rule indicates that HPMC has water holding capacity and converts free water to confined water. However, after 60 days of freezing, the height and area of T24 distribution increased to varying degrees, which indicated that the water state changed from restricted water to free-flowing state during the freezing process. This is mainly due to the change of the gluten protein conformation and the destruction of the "layer" unit in the gluten structure, which changes the state of the confined water contained in it. Walaupun kandungan air beku yang ditentukan oleh DSC juga meningkat dengan lanjutan masa penyimpanan pembekuan, bagaimanapun, disebabkan oleh perbezaan dalam kaedah pengukuran dan prinsip pencirian kedua -dua, air beku dan air bebas tidak sama sepenuhnya. For the wet gluten mass added with 2% HPMC, after 60 days of freezing storage, none of the four distributions showed significant differences, indicating that HPMC can effectively retain the water state due to its own water-holding properties and its interaction with gluten. and stable liquidity.
Secara umumnya, struktur protein sekunder dibahagikan kepada empat jenis, α-siral, β-dilipat, β-corner dan keriting rawak. The most important secondary bonds for the formation and stabilization of the spatial conformation of proteins are hydrogen bonds. Therefore, protein denaturation is a process of hydrogen bond breaking and conformational changes.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) has been widely used for high-throughput determination of the secondary structure of protein samples. The characteristic bands in the infrared spectrum of proteins mainly include, amide I band (1700.1600 cm-1), amide II band (1600.1500 cm-1) and amide III band (1350.1200 cm-1). Correspondingly, the amide I band the absorption peak originates from the stretching vibration of the carbonyl group (-C=O-.), the amide II band is mainly due to the bending vibration of the amino group (-NH-) [1271], and the amide III band is mainly due to the amino bending vibration and .CN-.Synchronous compound vibration in the same plane of bond stretching vibration, and has a high sensitivity to changes in protein secondary structure [128'1291. Walaupun tiga band ciri di atas adalah semua ciri-ciri inframerah penyerapan protein, spesifik dengan kata lain, intensiti penyerapan band amide II lebih rendah, jadi ketepatan separuh kuantitatif struktur sekunder protein adalah miskin; while the peak absorption intensity of amide I band is higher, so many researchers analyze the secondary structure of protein by this band [ 1301, but the absorption peak of water and the amide I band are overlapped at about 1640 cm. 1 wavenumber (Overlapped), which in turn affects the accuracy of the results. Therefore, the interference of water limits the determination of the amide I band in protein secondary structure determination. Dalam eksperimen ini, untuk mengelakkan gangguan air, kandungan relatif empat struktur sekunder protein gluten diperoleh dengan menganalisis band amide III. Peak position (wavenumber interval) of
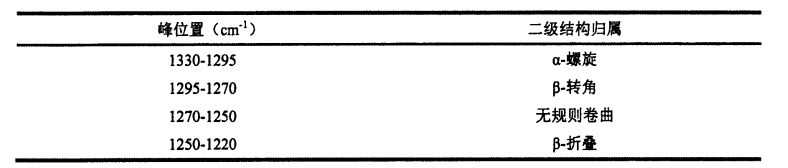
Figure 3.5 is the infrared spectrum of the amide III band of gluten protein added with different contents of HPMC for 0 days after being frozen for 0 days after deconvolution and fitting of the second derivative. (2001) applied the second derivative to fit the deconvoluted peaks with similar peak shapes [1321]. Untuk mengukur perubahan kandungan relatif setiap struktur sekunder, Jadual 3.5 meringkaskan kandungan peratusan relatif dari empat struktur sekunder protein gluten dengan masa pembekuan yang berlainan dan penambahan HPMC yang berbeza (kawasan puncak integral yang sepadan/kawasan puncak).
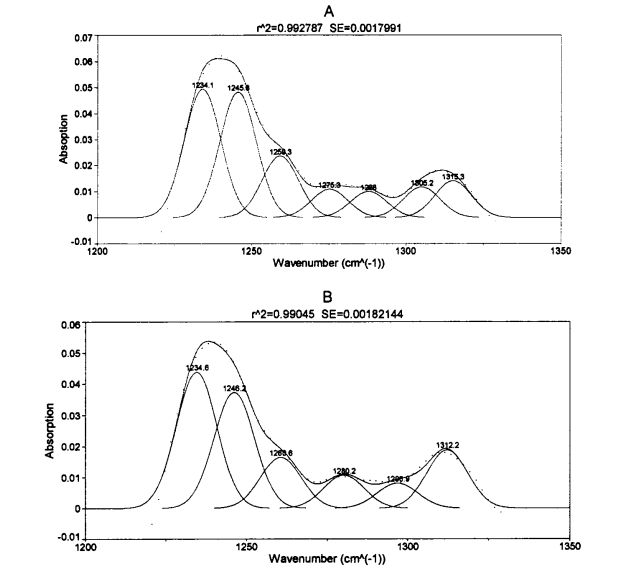
Note: A is the infrared spectrum of wheat gluten protein without adding HPMC for 0 days of frozen storage; B adalah spektrum inframerah protein gluten gandum penyimpanan beku selama 0 hari dengan 2% HPMC ditambah
With the prolongation of frozen storage time, the secondary structure of gluten protein with different additions of HPMC changed to different degrees. Ia dapat dilihat bahawa kedua -dua penyimpanan beku dan penambahan HPMC mempunyai kesan ke atas struktur sekunder protein gluten. Regardless of the amount of HPMC added, B. The folded structure is the most dominant structure, accounting for about 60%. After 60 days of frozen storage, add 0%, OB Gluten of 5% and 1% HPMC. The relative content of folds increased significantly by 3.66%, 1.87% and 1.16%, respectively, which was similar to the results determined by Meziani et al. (2011) [L33J]. Walau bagaimanapun, tidak terdapat perbezaan yang signifikan semasa penyimpanan beku untuk gluten ditambah dengan HPMC 2%. Di samping itu, apabila dibekukan selama 0 hari, dengan peningkatan tambahan HPMC, ms. Kandungan relatif lipatan meningkat sedikit, terutamanya apabila jumlah tambahan adalah 2%, ms. Kandungan relatif lipatan meningkat sebanyak 2.01%. D. Struktur yang dilipat boleh dibahagikan kepada p. Lipat (disebabkan oleh pengagregatan molekul protein), antiparallel p. Dilipat dan selari p. Tiga substruktur dilipat, dan sukar untuk menentukan substruktur mana yang berlaku semasa proses pembekuan
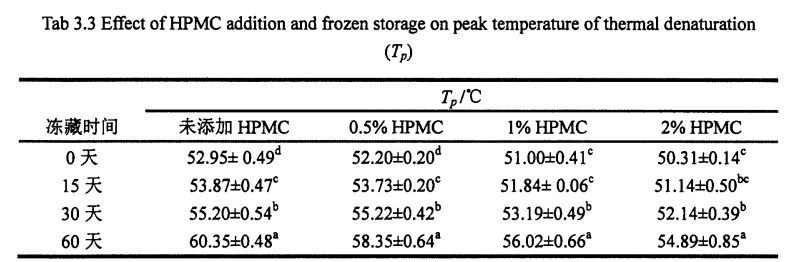
berubah. Some researchers believe that the increase in the relative content of the B-type structure will lead to an increase in the rigidity and hydrophobicity of the steric conformation [41], and other researchers believe that p. The increase in folded structure is due to part of the new β-Fold formation is accompanied by a weakening of the structural strength maintained by hydrogen bonding [421]. β- The increase in the folded structure indicates that the protein is polymerized through hydrophobic bonds, which is consistent with the results of the peak temperature of thermal denaturation measured by DSC and the distribution of transverse relaxation time measured by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Denaturasi protein. Sebaliknya, menambah 0.5%, 1% dan 2% protein gluten HPMC α-whirling. The relative content of helix increased by 0.95%, 4.42% and 2.03% respectively with the prolongation of freezing time, which is consistent with Wang, et a1. (2014) mendapati hasil yang sama [134]. 0 gluten tanpa menambah HPMC. There was no significant change in the relative content of helix during the frozen storage process, but with the increase of the addition amount of freeze for 0 days. There were significant differences in the relative content of α-whirling structures.
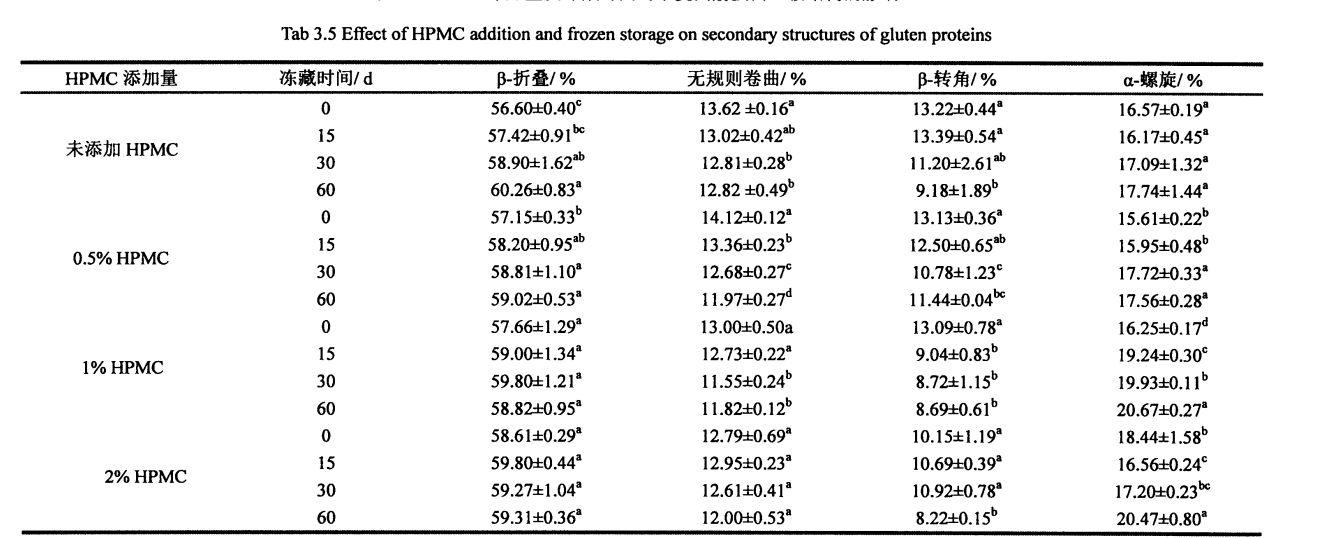
All samples with the extension of freezing time, p. The relative contents of the corners were significantly reduced. Ini menunjukkan bahawa β-giliran sangat sensitif terhadap rawatan pembekuan [135. 1361], dan sama ada HPMC ditambah atau tidak mempunyai kesan. Wellner, et a1. (2005) mencadangkan bahawa giliran rantaian protein gluten β berkaitan dengan struktur domain ruang β-giliran rantaian polipeptida glutenin [L 37]. Kecuali kandungan relatif struktur gegelung rawak protein gluten yang ditambah dengan 2% HPMC tidak mempunyai perubahan ketara dalam penyimpanan beku, sampel lain dikurangkan dengan ketara, yang mungkin disebabkan oleh penyemperitan kristal ais. In addition, when frozen for 0 days, the relative contents of α-helix, β-sheet and β-turn structure of gluten protein added with 2% HPMC were significantly different from those of gluten protein without HPMC. This may indicate that there is an interaction between HPMC and gluten protein, forming new hydrogen bonds and then affecting the conformation of the protein; atau HPMC menyerap air di rongga liang struktur ruang protein, yang mengubah bentuk protein dan membawa kepada lebih banyak perubahan antara subunit. Tutup. The increase of the relative content of β-sheet structure and the decrease of the relative content of β-turn and α-helix structure are consistent with the above speculation. During the freezing process, the diffusion and migration of water and the formation of ice crystals destroy the hydrogen bonds that maintain the conformational stability and expose the hydrophobic groups of proteins. In addition, from the perspective of energy, the smaller the energy of the protein, the more stable it is. At low temperature, the self-organization behavior (folding and unfolding) of protein molecules proceeds spontaneously and leads to conformational changes.
3.3.6 Kesan Jumlah Penambahan HPMC dan Masa Penyimpanan Pembekuan pada Permukaan Hidrofobisiti Protein Gluten
Molekul protein termasuk kedua -dua kumpulan hidrofilik dan hidrofobik. Umumnya, permukaan protein terdiri daripada kumpulan hidrofilik, yang boleh mengikat air melalui ikatan hidrogen untuk membentuk lapisan penghidratan untuk mencegah molekul protein dari aglomerating dan mengekalkan kestabilan konformasi mereka. The interior of the protein contains more hydrophobic groups to form and maintain the secondary and tertiary structure of the protein through the hydrophobic force. Denaturation of proteins is often accompanied by exposure of hydrophobic groups and increased surface hydrophobicity.
Tab3.6 Kesan penambahan HPMC dan penyimpanan beku pada hidrofobisiti permukaan gluten

3.3.7 Kesan Jumlah Penambahan HPMC dan Masa Penyimpanan Pembekuan pada Struktur Rangkaian Mikro Gluten
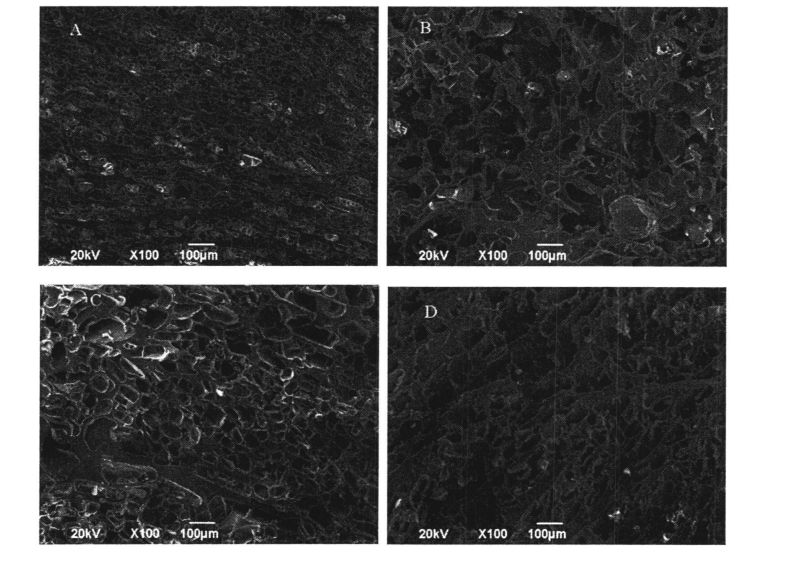
Nota: A ialah struktur mikro rangkaian gluten tanpa menambah HPMC dan beku selama 0 hari; B ialah struktur mikroskop rangkaian gluten tanpa menambah HPMC dan beku selama 60 hari; C is the microstructure of gluten network with 2% HPMC added and frozen for 0 days :D is the gluten network microstructure with 2% HPMC added and frozen for 60 days
Selepas 60 hari penyimpanan beku, mikrostruktur jisim gluten basah tanpa HPMC berubah dengan ketara (Rajah 3.7, AB). Pada 0 hari, struktur mikro gluten dengan 2% atau 0% HPMC menunjukkan bentuk lengkap, besar
Small approximate porous sponge-like morphology. Walau bagaimanapun, selepas 60 hari penyimpanan beku, sel -sel dalam mikrostruktur gluten tanpa HPMC menjadi saiz yang lebih besar, tidak teratur, dan diedarkan secara tidak rata (Rajah 3.7, a, b), terutamanya disebabkan oleh ini yang dibebaskan, yang konsisten dengan pengukuran itu, disulfide bond, which affects the strength and integrity of the structure. As reported by Kontogiorgos & Goff (2006) and Kontogiorgos (2007), the interstitial regions of the gluten network are squeezed due to freeze-shrinkage, resulting in structural disruption [138. 1391]. In addition, due to dehydration and condensation, a relatively dense fibrous structure was produced in the spongy structure, which may be the reason for the decrease in free thiol content after 15 days of frozen storage, because more disulfide bonds were generated and frozen storage. Struktur gluten tidak rosak teruk untuk masa yang lebih singkat, yang konsisten dengan Wang, et a1. (2014) mengamati fenomena yang sama [134]. At the same time, the destruction of the gluten microstructure leads to freer water migration and redistribution, which is consistent with the results of low-field time-domain nuclear magnetic resonance (TD-NMR) measurements. Some studies [140, 105] reported that after several freeze-thaw cycles, the gelatinization of rice starch and the structural strength of the dough became weaker, and the water mobility became higher. Nonetheless, after 60 days of frozen storage, the microstructure of gluten with 2% HPMC addition changed less, with smaller cells and more regular shapes than gluten without HPMC addition (Fig. 3.7, B, D). Ini selanjutnya menunjukkan bahawa HPMC secara berkesan dapat menghalang pemusnahan struktur gluten dengan penghabluran semula.
3.4 Ringkasan Bab
This experiment investigated the rheology of wet gluten dough and gluten protein by adding HPMC with different contents (0%, 0.5%, 1% and 2%) during freezing storage (0, 15, 30 and 60 days). properties, thermodynamic properties, and effects of physicochemical properties. Kajian mendapati bahawa perubahan dan pengagihan semula keadaan air semasa proses penyimpanan pembekuan dengan ketara meningkatkan kandungan air beku dalam sistem gluten basah, yang menyebabkan pemusnahan struktur gluten disebabkan oleh pembentukan dan pertumbuhan kristal ais, dan akhirnya menyebabkan sifat pemprosesan doh menjadi berbeza. Deterioration of product quality. Hasil pengimbasan kekerapan menunjukkan bahawa modulus elastik dan modulus likat jisim gluten basah tanpa menambah HPMC menurun dengan ketara semasa proses penyimpanan pembekuan, dan mikroskop elektron pengimbasan menunjukkan bahawa mikrostrukturnya telah rosak. The content of free sulfhydryl group was significantly increased, and its hydrophobic group was more exposed, which made the thermal denaturation temperature and surface hydrophobicity of gluten protein significantly increased. However, the experimental results show that the addition of I-IPMC can effectively inhibit the changes in the structure and properties of wet gluten mass and gluten protein during freezing storage, and within a certain range, this inhibitory effect is positively correlated with the addition of HPMC. This is because HPMC can reduce the mobility of water and limit the increase of the freezable water content, thereby inhibiting the recrystallization phenomenon and keeping the gluten network structure and the spatial conformation of the protein relatively stable. Ini menunjukkan bahawa penambahan HPMC dapat mengekalkan integriti struktur doh beku, dengan itu memastikan kualiti produk.
Bab 4 Kesan penambahan HPMC pada struktur dan sifat kanji di bawah penyimpanan beku
4.1 Pengenalan
Pati adalah salah satu komponen utama tepung, dan kandungannya setinggi kira -kira 75% (kering). Pada masa yang sama, sebagai karbohidrat yang banyak hadir dalam bijirin, kanji juga merupakan bahan sumber tenaga utama dalam makanan. Dalam sistem doh, kanji kebanyakannya diedarkan dan dilampirkan pada struktur rangkaian protein gluten. During processing and storage, starches often undergo gelatinization and aging stages.
Among them, starch gelatinization refers to the process in which starch granules are gradually disintegrated and hydrated in a system with high water content and under heating conditions. It can be roughly divided into three main processes. 1) Reversible water absorption stage; before reaching the initial temperature of gelatinization, the starch granules in the starch suspension (Slurry) keep their unique structure unchanged, and the external shape and internal structure basically do not change. Hanya kanji larut yang sangat sedikit tersebar di dalam air dan boleh dipulihkan ke keadaan asalnya. 2) peringkat penyerapan air yang tidak dapat dipulihkan; as the temperature increases, water enters the gap between the starch crystallite bundles, irreversibly absorbs a large amount of water, causing the starch to swell, the volume expands several times, and the hydrogen bonds between the starch molecules are broken. It becomes stretched and the crystals disappear. At the same time, the birefringence phenomenon of starch, that is, the Maltese Cross observed under a polarizing microscope, begins to disappear, and the temperature at this time is called the initial gelatinization temperature of starch. 3) Starch granule disintegration stage; starch molecules completely enter the solution system to form starch paste (Paste/Starch Gel), at this time the viscosity of the system is the largest, and the birefringence phenomenon completely disappears, and the temperature at this time is called the complete starch gelatinization temperature, the gelatinized starch is also called α-starch [141]. When the dough is cooked, the gelatinization of starch endows the food with its unique texture, flavor, taste, color, and processing characteristics.
Secara umum, gelatinisasi kanji dipengaruhi oleh sumber dan jenis kanji, kandungan relatif amilosa dan amilopektin dalam kanji, sama ada kanji diubahsuai dan kaedah pengubahsuaian, penambahan bahan eksogen lain, dan keadaan penyebaran (seperti pengaruh spesies ion garam dan kepekatan, pH, suhu, kandungan kelembapan, dan sebagainya. Oleh itu, apabila struktur kanji (morfologi permukaan, struktur kristal, dan lain -lain) diubah, sifat gelatinisasi, sifat rheologi, sifat penuaan, kecernaan, dan lain -lain kanji akan terjejas dengan sewajarnya.
In this experiment, by adding different HPMC contents (0, 0.5%, 1%, 2%) to the starch suspension, the amount of HPMC added during a certain freezing period (0, 15, 30, 60 days) was studied. pada struktur kanji dan pengaruh gelatinisasi alam semula jadi.
Kanji gandum Binzhou Zhongyu Food Co., Ltd.; HPMC Aladdin (Shanghai) Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.;
Nama peralatan
BSAL24S Baki elektronik
BC/BD-272SC peti sejuk
DHG. Ketuhar pengeringan letupan 9070A
Pengilang
Sartorius, Jerman
Hefei Meiling Co., Ltd.
American TA Company
American TA Company
Ambil sampel yang disebutkan di atas yang dirawat dengan masa pembekuan yang sepadan, menyeimbangkan pada 4 ° C selama 4 jam, dan kemudian pindah ke suhu bilik sehingga mereka benar-benar dicairkan.
(1) Ciri -ciri gelatinisasi kanji
Dalam eksperimen ini, rheometer digunakan bukannya viscometer yang cepat untuk mengukur ciri -ciri gelatinisasi kanji. See Bae et a1. (2014) method [1571] with slight modifications. The specific program parameters are set as follows: use a plate with a diameter of 40 mill, the gap (gap) is 1000 mm, and the rotation speed is 5 rad/s; I) incubate at 50 °C for 1 min; ii) at 5. C/min heated to 95°C; iii) kept at 95°C for 2.5 min, iv) then cooled to 50°C at 5°C/min; v) Terakhir diadakan pada 50 ° C selama 5 minit.
Draw 1.5 mL of sample solution and add it to the center of the rheometer sample stage, measure the gelatinization properties of the sample according to the above program parameters, and obtain the time (min) as the abscissa, the viscosity (Pa s) and the temperature (°C) as the starch gelatinization curve of the ordinate. According to GB/T 14490.2008 [158], the corresponding gelatinization characteristic indicators—gelatinization peak viscosity (field), peak temperature (Ang), minimum viscosity (high), final viscosity (ratio) and decay value (Breakdown) are obtained. Nilai, bv) dan nilai regenerasi (nilai kemunduran, sv), di mana, nilai kerosakan = kelikatan puncak - kelikatan minimum; setback value = final viscosity - minimum viscosity. Each sample was repeated three times.
4.2.3.3 Properti Gel Pati Pati
Ambil 2.5 g amiloid dan campurkan dengan air suling dalam nisbah 1: 2 untuk membuat susu kanji. Membekukan pada 18 ° C selama 15 d, 30 d, dan 60 d. Tambah 0.5, 1, 2% HPMC (w/w) untuk menggantikan kanji dengan kualiti yang sama, dan kaedah penyediaan lain tetap tidak berubah. Selepas rawatan pembekuan selesai, ambilnya, nyatakan pada 4 ° C selama 4 jam, dan kemudian cair pada suhu bilik sehingga ia diuji.
Then, sweep the oscillation frequency, set the strain amount (strain) to 0.1% (according to the strain sweep results), and set the frequency range to O. 1 to 10 Hz. Setiap sampel diulang tiga kali.
Selepas masa rawatan pembekuan yang sama, sampel telah dikeluarkan, dicairkan sepenuhnya, dan dikeringkan dalam ketuhar pada 40 ° C selama 48 jam. Akhirnya, ia adalah tanah melalui penapis 100 mesh untuk mendapatkan sampel serbuk pepejal untuk digunakan (sesuai untuk ujian XRD). Lihat Xie, et a1. (2014) method for sample preparation and determination of thermodynamic properties '1611, weigh 10 mg of starch sample into a liquid aluminum crucible with an ultra-micro analytical balance, add 20 mg of distilled water in a ratio of 1:2, press and seal it and place it at 4 °C In the refrigerator, equilibrated for 24 h. Membekukan pada 18 ° C (0, 15, 30 dan 60 hari). Tambah 0.5%, 1%, 2%(w/w) HPMC untuk menggantikan kualiti kanji yang sepadan, dan kaedah penyediaan lain kekal tidak berubah. After the freezing storage time is over, take out the crucible and equilibrate at 4 °C for 4 h.
The thawed frozen starch samples were dried in an oven at 40 °C for 48 h, then ground and sieved through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain starch powder samples. Take a certain amount of the above samples, use D/MAX 2500V type X. The crystal form and relative crystallinity were determined by X-ray diffractometer. Parameter eksperimen adalah voltan 40 kV, semasa 40 Ma, menggunakan Cu. KS sebagai Sumber X. Ray. At room temperature, the scanning angle range is 30--400, and the scanning rate is 20/min. Relative crystallinity (%) = crystallization peak area/total area x 100%, where the total area is the sum of the background area and the peak integral area [1 62].
4.2.3.6 Penentuan Kuasa Bengkak Kanji
All experiments were repeated at least three times unless otherwise specified, and the experimental results were expressed as mean and standard deviation. SPSS Statistic 19 was used for analysis of variance (Analysis of Variance, ANOVA) with a significance level of 0.05; Carta korelasi telah diambil menggunakan asal 8.0.
4.3 Analisis dan Perbincangan
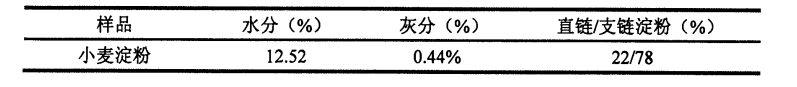
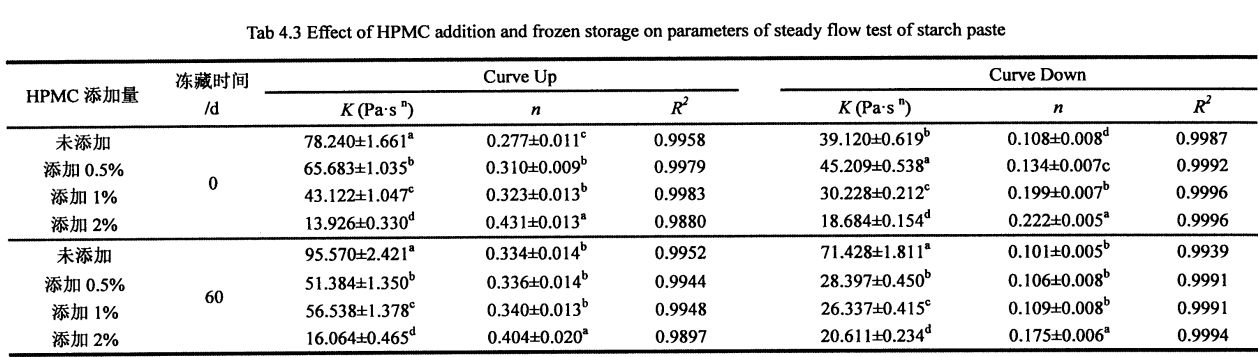
4.3.2 Kesan jumlah tambahan HPMC dan masa penyimpanan beku pada ciri -ciri gelatinisasi kanji gandum
Penggantungan kanji dengan kepekatan tertentu dipanaskan pada kadar pemanasan tertentu untuk membuat gelatinized kanji. After starting to gelatinize, the turbid liquid gradually becomes pasty due to the expansion of starch, and the viscosity increases continuously. Seterusnya, granul kanji pecah dan kelikatan berkurangan. When the paste is cooled at a certain cooling rate, the paste will gel, and the viscosity value will further increase. The viscosity value when it is cooled to 50 °C is the final viscosity value (Figure 4.1).
Jadual 4.2 menyenaraikan pengaruh beberapa petunjuk penting ciri -ciri gelatinisasi kanji, termasuk kelikatan puncak gelatinisasi, kelikatan minimum, kelikatan akhir, nilai kerosakan dan nilai penghargaan, dan mencerminkan kesan tambahan HPMC dan masa pembekuan pada tampalan kanji. effects of chemical properties. Hasil eksperimen menunjukkan bahawa kelikatan puncak, kelikatan minimum dan kelikatan akhir kanji tanpa penyimpanan beku meningkat dengan ketara dengan peningkatan penambahan HPMC, sementara nilai pereputan dan nilai pemulihan menurun dengan ketara. Specifically, the peak viscosity gradually increased from 727.66+90.70 CP (without adding HPMC) to 758.51+48.12 CP (adding 0.5% HPMC), 809.754-56.59 CP (adding 1 %HPMC), and 946.64+9.63 CP (adding 2% HPMC); the minimum viscosity was increased from 391.02+18.97 CP (blank not adding) to 454.95+36.90 (adding O .5% HPMC), 485.56+54.0.5 (add 1% HPMC) and 553.03+55.57 CP (add 2% HPMC); the final viscosity is from 794.62.412.84 CP ( Without adding HPMC) increased to 882.24±22.40 CP (adding 0.5% HPMC), 846.04+12.66 CP (adding 1% HPMC) and 910.884-34.57 CP (adding 2 %HPMC); however, the attenuation value gradually decreased from 336.644-71.73 CP (without adding HPMC) to 303.564-11.22 CP (adding 0.5% HPMC), 324.19±2.54 CP (Add
With 1% HPMC) and 393.614-45.94 CP (with 2% HPMC), the retrogradation value decreased from 403.60+6.13 CP (without HPMC) to 427.29+14.50 CP, respectively (0.5% HPMC added), 360.484-41.39 CP (15 HPMC added) and 357.85+21.00 CP (2% HPMC ditambah). This and the addition of hydrocolloids such as xanthan gum and guar gum obtained by Achayuthakan & Suphantharika (2008) and Huang (2009) can increase the gelatinization viscosity of starch while reducing the retrogradation value of starch. This may be mainly because HPMC acts as a kind of hydrophilic colloid, and the addition of HPMC increases the gelatinization peak viscosity due to the hydrophilic group on its side chain which makes it more hydrophilic than starch granules at room temperature. In addition, the temperature range of the thermal gelatinization process (thermogelation process) of HPMC is larger than that of starch (results not shown), so that the addition of HPMC can effectively suppress the drastic decrease in viscosity due to the disintegration of starch granules. Therefore, the minimum viscosity and final viscosity of starch gelatinization increased gradually with the increase of HPMC content.
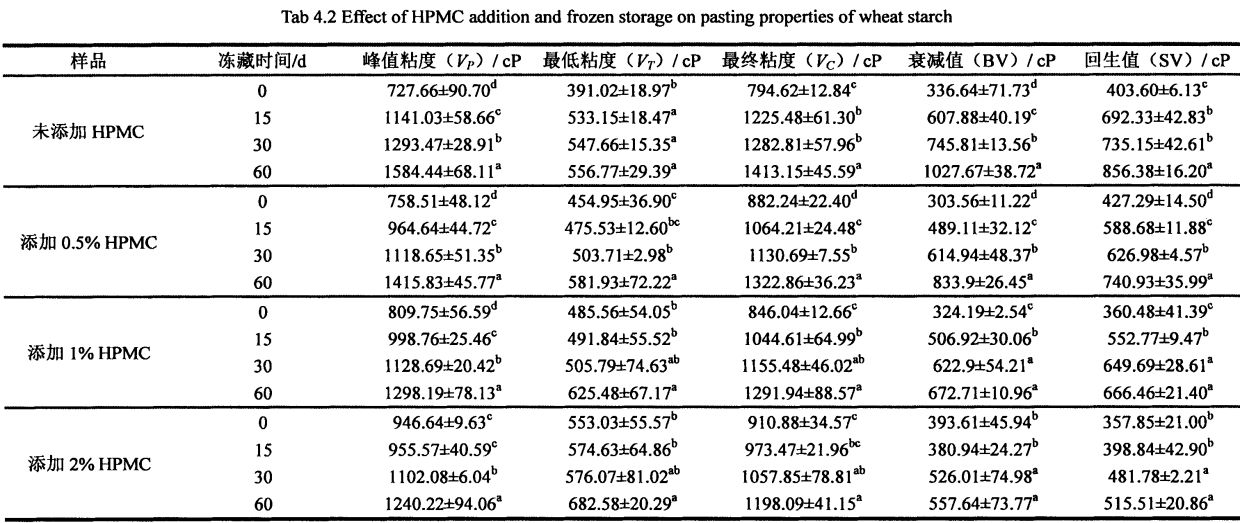
P (frozen storage for 0 days) to 856.38 ± 16.20 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); Nilai retrogradasi penggantungan kanji ditambah dengan 0.5% HPMC meningkat daripada 427 .29 ± 14.50 cp (penyimpanan beku selama 0 hari) meningkat kepada 740.93 ± 35.99 cp (penyimpanan beku selama 60 hari); the retrogradation value of starch suspension added with 1% HPMC increased from 360.48±41. 39 cp (penyimpanan beku selama 0 hari) meningkat kepada 666.46 ± 21.40 cp (penyimpanan beku selama 60 hari); while the retrogradation value of starch suspension added with 2% HPMC increased from 357.85 ± 21.00 CP (frozen storage for 60 days). 0 days) increased to 515.51 ± 20.86 CP (60 days frozen).
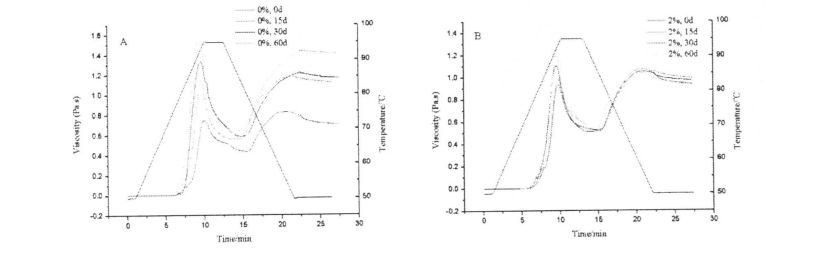
Rajah 4 .1 Menyisipkan lengkung kanji gandum tanpa hpmc (a) atau dengan 2 % hpmc①)
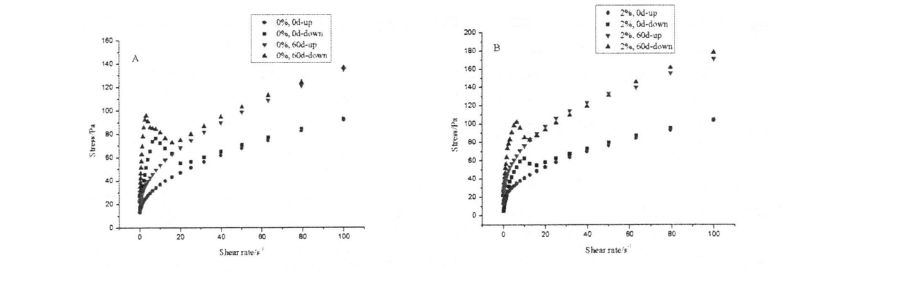
Rajah 4.2 Thixotropism Pati Pati tanpa HPMC (A) atau dengan 2 % HPMC (B)
Ia dapat dilihat dari Jadual 4.3 bahawa semua indeks ciri aliran, 2, kurang daripada 1. Oleh itu, pasta kanji (sama ada HPMC ditambah atau sama ada ia dibekukan atau tidak) tergolong dalam cecair pseudoplastik, dan semua menunjukkan fenomena penipisan ricih (apabila kadar ricih meningkat, viscosity ricih dari penurunan cecair). Di samping itu, imbasan kadar ricih berkisar antara 0.1 s. 1 meningkat kepada 100 s ~, dan kemudian menurun dari 100 SD ke O. Kurva rheologi yang diperoleh pada 1 SD tidak sepenuhnya bertindih, dan hasil yang sesuai k, s juga berbeza, jadi pasta kanji adalah cecair pseudoplastik thixotropic (sama ada HPMC ditambah atau sama ada ia dibekukan atau tidak). However, under the same freezing storage time, with the increase of HPMC addition, the difference between the fitting results of the K n values of the two scans gradually decreased, which indicates that the addition of HPMC makes the structure of starch paste under shear stress. Ia tetap stabil di bawah tindakan dan mengurangkan "cincin thixotropic"
On the other hand, for the starch without frozen storage, its K value decreased significantly with the addition of HPMC, from 78.240±1.661 Pa ·sn (without adding HPMC) to 65.240±1.661 Pa ·sn (without adding HPMC), respectively. 683±1.035 Pa ·sn (add 0.5% Hand MC), 43.122±1.047 Pa ·sn (add 1% HPMC), and 13.926±0.330Pa·Sn (add 2% HPMC), while the n value increased significantly, from 0.277 ± 0.011 (without adding HPMC) to 0.277 ± 0.011 in turn. 310 ± 0.009 (add 0.5% HPMC), O. 323 ± 0.013 (add 1% HPMC) and O. 43 1 ± 0.0 1 3 (adding 2% HPMC), which is similar to the experimental results of Techawipharat, Suphantharika, & BeMiller (2008) and Turabi, Sumnu, & Sahin (2008), and the increase of n value shows that the addition of HPMC makes the fluid has a tendency to change from pseudoplastic to Newtonian [168'1691]. Pada masa yang sama, untuk kanji yang disimpan beku selama 60 hari, nilai k, n menunjukkan peraturan perubahan yang sama dengan peningkatan penambahan HPMC.
Walau bagaimanapun, dengan pemanjangan masa penyimpanan pembekuan, nilai k dan n meningkat kepada darjah yang berbeza, di antaranya nilai K meningkat dari 78.240 ± 1.661 PA · SN (tidak disesuaikan, 0 hari) hingga 95.570 ± 1. 2.421 Pa·sn (no addition, 60 days), increased from 65.683±1.035 Pa ·S n (addition of O. 5% HPMC, 0 days) to 51.384±1.350 Pa ·S n (Add to 0.5% HPMC, 60 days), increased from 43.122±1.047 Pa ·sn (adding 1% HPMC, 0 days) to 56.538±1.378 Pa ·sn (adding 1% HPMC, 60 days) ), and increased from 13.926 ± 0.330 Pa ·sn (adding 2% HPMC, 0 days) to 16.064 ± 0.465 Pa ·sn (adding 2% HPMC, 60 days); 0.277 ± 0.011 (tanpa menambah HPMC, 0 hari) meningkat kepada O. 334 ± 0.014 (tiada tambahan, 60 hari), meningkat dari 0.310 ± 0.009 (0.5% HPMC ditambah, 0 hari) 0.340 ± 0.013 (add 1% HPMC, 60 days), and from 0.431 ± 0.013 (add 1% HPMC, 60 days) 2% HPMC, 0 days) to 0.404+0.020 (add 2% HPMC, 60 days). Sebagai perbandingan, dapat dijumpai bahawa dengan peningkatan jumlah tambahan HPMC, kadar perubahan K dan nilai pisau berkurangan berturut -turut, yang menunjukkan bahawa penambahan HPMC dapat membuat tampalan kanji stabil di bawah tindakan daya ricih, yang konsisten dengan hasil pengukuran ciri -ciri gelatinisasi kanji. konsisten.
The starch gelatinization process is accompanied by the disintegration of starch granules, the disappearance of the crystalline region, and the hydrogen bonding between starch chains and moisture, the starch gelatinized to form a heat-induced (Heat. induced) gel with a certain gel strength. As shown in Figure 4.3, for starch without frozen storage, with the increase of HPMC addition, the G' of starch decreased significantly, while G" had no significant difference, and tan 6 increased (Liquid. 1ike), which shows that during the gelatinization process, HPMC interacts with starch, and due to the water retention of HPMC, the addition of HPMC reduces the water loss of starch during the gelatinization process. At the same time, Chaisawang & Suphantharika (2005) found that, adding guar gum and xanthan gum to tapioca starch, the G' of the starch paste also decreased [170]. In addition, with the extension of the freezing storage time, the G' of starch gelatinized decreased to different degrees. This is mainly because during the frozen storage process of starch, the amylose in the amorphous region of starch granules is separated to form damaged starch (Damaged Starch), which reduces the degree of intermolecular cross-linking after starch gelatinization and the degree of cross-linking after cross-linking. Stability and compactness, and the physical extrusion of ice crystals makes the arrangement of "micelles" (microcrystalline structures, mainly composed of amylopectin) in the starch crystallization area more compact, increasing the relative crystallinity of starch, and at the same time , resulting in insufficient combination of molecular chain and water after starch gelatinization, low extension of molecular chain (molecular chain mobility), and finally caused the gel strength of starch to decline. Walau bagaimanapun, dengan peningkatan penambahan HPMC, trend penurunan G 'ditindas, dan kesan ini berkorelasi positif dengan penambahan HPMC. This indicated that the addition of HPMC could effectively inhibit the effect of ice crystals on the structure and properties of starch under frozen storage conditions.
The swelling ratio of starch can reflect the size of starch gelatinization and water swelling, and the stability of starch paste under centrifugal conditions. As shown in Figure 4.4, for starch without frozen storage, with the increase of HPMC addition, the swelling force of starch increased from 8.969+0.099 (without adding HPMC) to 9.282- -L0.069 (adding 2% HPMC), which shows that the addition of HPMC increases the swelling water absorption and makes starch more stable after gelatinization, which is consistent with the Kesimpulan ciri -ciri gelatinisasi kanji. However, with the extension of frozen storage time, the swelling power of starch decreased. Compared with 0 days of frozen storage, the swelling power of starch decreased from 8.969-a:0.099 to 7.057+0 after frozen storage for 60 days, respectively. .007 (no HPMC added), reduced from 9.007+0.147 to 7.269-4-0.038 (with O.5% HPMC added), reduced from 9.284+0.157 to 7.777 +0.014 (adding 1% HPMC), reduced from 9.282+0.069 to 8.064+0.004 (adding 2% HPMC). The results showed that the starch granules were damaged after freezing storage, resulting in the precipitation of part of the soluble starch and centrifugation. Therefore, the solubility of starch increased and the swelling power decreased. In addition, after freezing storage, starch gelatinized starch paste, its stability and water holding capacity decreased, and the combined action of the two reduced the swelling power of starch [1711]. On the other hand, with the increase of HPMC addition, the decline of starch swelling power gradually decreased, indicating that HPMC can reduce the amount of damaged starch formed during freezing storage and inhibit the degree of starch granule damage.
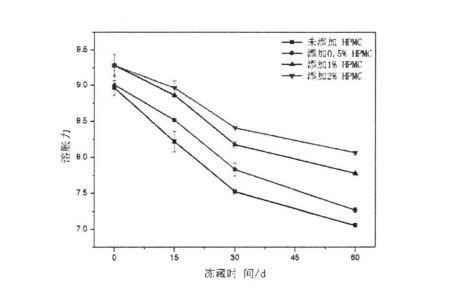
Rajah 4.4 Kesan penambahan HPMC dan penyimpanan beku pada kuasa bengkak kanji
4.3.6 Kesan jumlah tambahan HPMC dan masa penyimpanan beku pada sifat termodinamik kanji
Gelatinisasi kanji adalah proses termodinamik kimia endotermik. Therefore, DSC is often used to determine the onset temperature (Dead), peak temperature (To), end temperature (T p), and gelatinization enthalpy of starch gelatinization. (Tc). Jadual 4.4 menunjukkan lengkung DSC gelatinisasi kanji dengan 2% dan tanpa HPMC ditambah untuk masa penyimpanan pembekuan yang berbeza.
As shown in Table 4.4, for fresh amyloid, with the increase of HPMC addition, starch L has no significant difference, but increases significantly, from 77.530 ± 0.028 (without adding HPMC) to 78.010 ± 0.042 (add 0.5% HPMC), 78.507 ± 0.051 (add 1% HPMC), and 78.606 ± 0.034 (add 2% HPMC), but 4H is significant Decrease, from 9.450 ± 0.095 (without adding HPMC) to 8.53 ± 0.030 (adding 0.5% HPMC), 8.242A: 0.080 (adding 1% HPMC) and 7 .736 ± 0.066 (add 2% HPMC). Ini serupa dengan Zhou, et a1. (2008) found that adding a hydrophilic colloid decreased the starch gelatinization enthalpy and increased the starch gelatinization peak temperature [172]. Ini terutamanya kerana HPMC mempunyai hidrofilik yang lebih baik dan lebih mudah digabungkan dengan air daripada kanji. At the same time, due to the large temperature range of the thermally accelerated gelation process of HPMC, the addition of HPMC increases the peak gelatinization temperature of starch, while the gelatinization Enthalpy decreases.
Sebaliknya, gelatinisasi kanji ke, t p, tc, △ t dan △ Hall meningkat dengan lanjutan masa pembekuan. Specifically, starch gelatinization with 1% or 2% HPMC added had no significant difference after freezing for 60 days, while starch without or with 0.5% HPMC was added from 68.955±0.01 7 (frozen storage for 0 days) increased to 72.340 ± 0.093 (frozen storage for 60 days), and from 69.170 ± 0.035 (frozen storage for 0 days) to 71.613 ± 0.085 (frozen storage for 0 days) 60 days); after 60 days of frozen storage, the growth rate of starch gelatinization decreased with the increase of HPMC addition, such as starch without HPMC added from 77.530 ± 0.028 (frozen storage for 0 days) to 81.028. 408 ± 0.021 (frozen storage for 60 days), while the starch added with 2% HPMC increased from 78.606 ± 0.034 (frozen storage for 0 days) to 80.017 ± 0.032 (frozen storage for 60 days). days); in addition, ΔH also showed the same change rule, which increased from 9.450 ± 0.095 (no addition, 0 days) to 12.730 ± 0.070 (no addition, 60 days), respectively, from 8.450 ± 0.095 (no addition, 0 days) to 12.730 ± 0.070 (no addition, 60 days), respectively. 531 ± 0.030 (add 0.5%, 0 days) to 11.643 ± 0.019 (add 0.5%, 60 days), from 8.242 ± 0.080 (add 1%, 0 days) to 10.509 ± 0.029 (add 1%, 60 days), and from 7.736 ± O. 066 (2% addition, 0 days) rose to 9.450 ± 0.093 (2% addition, 60 days). Sebab-sebab utama perubahan yang disebutkan di atas dalam sifat termodinamik gelatinisasi kanji semasa proses penyimpanan beku adalah pembentukan kanji yang rosak, yang memusnahkan rantau amorf (rantau amorf) dan meningkatkan kristal di rantau kristal. Bersama -sama kedua -dua meningkatkan kristal relatif kanji, yang seterusnya membawa kepada peningkatan indeks termodinamik seperti suhu puncak gelatinisasi kanji dan entalpi gelatinisasi. However, through comparison, it can be found that under the same freezing storage time, with the increase of HPMC addition, the increase of starch gelatinization To, T p, Tc, ΔT and ΔH gradually decreases. It can be seen that the addition of HPMC can effectively maintain the relative stability of the starch crystal structure, thereby inhibiting the increase of the thermodynamic properties of starch gelatinization.
Figure 4.6. As shown in A, the positions of the starch crystallization peaks are located at 170, 180, 190 and 230, respectively, and there is no significant change in the peak positions regardless of whether they are treated by freezing or adding HPMC. Ini menunjukkan bahawa, sebagai harta intrinsik penghabluran kanji gandum, bentuk kristal tetap stabil.
Rajah 4.6 Kesan penambahan HPMC dan penyimpanan beku pada sifat XRD
Note: A is x. Corak difraksi sinar-X; B is the relative crystallinity result of starch;
4.4 Ringkasan Bab
Starch is the most abundant dry matter in dough, which, after gelatinization, adds unique qualities (specific volume, texture, sensory, flavor, etc.) to the dough product. Since the change of starch structure will affect its gelatinization characteristics, which will also affect the quality of flour products, in this experiment, the gelatinization characteristics, flowability and flowability of starch after frozen storage were investigated by examining starch suspensions with different contents of HPMC added. Changes in rheological properties, thermodynamic properties and crystal structure were used to evaluate the protective effect of HPMC addition on starch granule structure and related properties. The experimental results showed that after 60 days of frozen storage, the starch gelatinization characteristics (peak viscosity, minimum viscosity, final viscosity, decay value and retrogradation value) all increased due to the significant increase in the relative crystallinity of starch and the increase in the content of damaged starch. Entalpi gelatinisasi meningkat, manakala kekuatan gel pati kanji menurun dengan ketara; however, especially the starch suspension added with 2% HPMC, the relative crystallinity increase and starch damage degree after freezing were lower than those in the control group Therefore, the addition of HPMC reduces the degree of changes in gelatinization characteristics, gelatinization enthalpy, and gel strength, which indicates that the addition of HPMC keeps the starch structure and its gelatinization properties relatively stable.
Yeast has a wide range of applications in fermented flour products (sourdough is obtained by natural fermentation, mainly lactic acid bacteria), it can use the hydrolyzed product of starch in the dough - glucose or maltose as a carbon source, under aerobic conditions, using Substances produce carbon dioxide and water after respiration. Karbon dioksida yang dihasilkan boleh membuat doh longgar, berliang dan besar. At the same time, the fermentation of yeast and its role as an edible strain can not only improve the nutritional value of the product, but also significantly improve the flavor characteristics of the product. Therefore, the survival rate and fermentation activity of yeast have an important impact on the quality of the final product (specific volume, texture, and flavor, etc.) [175].
In the case of frozen storage, yeast will be affected by environmental stress and affect its viability. When the freezing rate is too high, the water in the system will rapidly crystallize and increase the external osmotic pressure of the yeast, thereby causing the cells to lose water; Apabila kadar pembekuan terlalu tinggi. If it is too low, the ice crystals will be too large and the yeast will be squeezed and the cell wall will be damaged; Kedua -duanya akan mengurangkan kadar survival yis dan aktiviti penapaiannya. In addition, many studies have found that after the yeast cells are ruptured due to freezing, they will release a reducing substance-reduced glutathione, which in turn reduces the disulfide bond to a sulfhydryl group, which will eventually destroy the network structure of gluten protein, resulting in a decrease in the quality of pasta products [176-177].
BPS. Kotak malar dan kelembapan 500CL
ZWY-240 Inkubator Suhu Tetap
BDS. 200 mikroskop biologi terbalik
Pengilang
Angel Yeast Co., Ltd.
Chongqing Auto Optical Instrument Co., Ltd.
5.2.2 Kaedah Eksperimen
5.2.2.2 Ketinggian Pemeriksaan Doh
See Meziani, et a1. (2012)'s experimental method [17 cited, with slight modifications. Weigh 5 g of frozen dough into a 50 mL colorimetric tube, press the dough to a uniform height of 1.5 cm at the bottom of the tube, then place it upright in a constant temperature and humidity box, and incubate for 1 h at 30 °C and 85% RH, after taking it out, measure the proofing height of the dough with a millimeter ruler (retain two digits after the decimal point). Untuk sampel dengan hujung atas yang tidak sekata selepas pemeriksaan, pilih 3 atau 4 mata pada selang masa yang sama untuk mengukur ketinggian yang sama (contohnya, setiap 900), dan nilai ketinggian yang diukur adalah purata. Each sample was paralleled three times.
Kaedah alloxan digunakan untuk menentukan kandungan glutathione. Prinsipnya ialah produk tindak balas glutathione dan alloxan mempunyai puncak penyerapan pada 305 nl. Specific determination method: pipette 5 mL of yeast solution into a 10 mL centrifuge tube, then centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 10 min, take 1 mL of supernatant into a 10 mL centrifuge tube, add 1 mL of 0.1 mol/mL to the tube L alloxan solution, mixed thoroughly, then add 0.2 M PBS (pH 7.5) and 1 mL of 0.1 M, NaOH solution to it, mix well, let stand for 6 min, and immediately add 1 M, NaOH The solution was 1 mL, and the absorbance at 305 nm was measured with a UV spectrophotometer after thorough mixing. The glutathione content was calculated from the standard curve. Each sample was paralleled three times.
5.2.2.5 Pemprosesan Data
5.3 Hasil dan perbincangan
Ketinggian adunan yang sering dipengaruhi oleh kesan gabungan aktiviti pengeluaran gas penapaian yis dan kekuatan struktur rangkaian doh. Among them, yeast fermentation activity will directly affect its ability to ferment and produce gas, and the amount of yeast gas production determines the quality of fermented flour products, including specific volume and texture. The fermentation activity of yeast is mainly affected by external factors (such as changes in nutrients such as carbon and nitrogen sources, temperature, pH, etc.) and internal factors (growth cycle, activity of metabolic enzyme systems, etc.).

Rajah 5.2 Kesan penambahan HPMC dan penyimpanan beku pada kadar survival yis
It can be seen from Figure 5.2 that there is no significant difference in the number of yeast colonies in samples with different contents of HPMC added without freezing treatment. Ini sama dengan hasil yang ditentukan oleh Heitmann, Zannini, & Arendt (2015) [180]. Walau bagaimanapun, selepas 60 hari pembekuan, bilangan koloni yis menurun dengan ketara, dari 3.08x106 CFU hingga 1.76x106 CFU (tanpa menambah HPMC); from 3.04x106 CFU to 193x106 CFU (adding 0.5% HPMC); reduced from 3.12x106 CFU to 2.14x106 CFU (added 1% HPMC); reduced from 3.02x106 CFU to 2.55x106 CFU (added 2% HPMC). Sebagai perbandingan, dapat dijumpai bahawa tekanan persekitaran penyimpanan pembekuan menyebabkan penurunan bilangan koloni yis, tetapi dengan peningkatan penambahan HPMC, tahap penurunan jumlah koloni menurun. This indicates that HPMC can better protect yeast under freezing conditions. Mekanisme perlindungan mungkin sama dengan gliserol, antibeku terikan yang biasa digunakan, terutamanya dengan menghalang pembentukan dan pertumbuhan kristal ais dan mengurangkan tekanan persekitaran suhu rendah kepada yis. Rajah 5.3 adalah photomicrograph yang diambil dari sekeping ujian pengiraan Rapid 3m selepas penyediaan dan pemeriksaan mikroskopik, yang selaras dengan morfologi luaran yis.
Rajah 5 .3 Mikrograf ragi
Glutathione is a tripeptide compound composed of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine, and has two types: reduced and oxidized. When the yeast cell structure is destroyed and died, the permeability of the cells increases, and the intracellular glutathione is released to the outside of the cell, and it is reductive. Sangat perlu diperhatikan bahawa glutation yang dikurangkan akan mengurangkan ikatan disulfida (-ss-) yang dibentuk oleh silang silang protein gluten, memecahkannya untuk membentuk kumpulan sulfhydryl percuma (.sh), yang seterusnya mempengaruhi struktur rangkaian doh. stability and integrity, and ultimately lead to the deterioration of the quality of fermented flour products. Usually, under environmental stress (such as low temperature, high temperature, high osmotic pressure, etc.), yeast will reduce its own metabolic activity and increase its stress resistance, or produce spores at the same time. Apabila keadaan alam sekitar sesuai untuk pertumbuhan dan pembiakannya lagi, kemudian memulihkan metabolisme dan kecergasan proliferasi. However, some yeasts with poor stress resistance or strong metabolic activity will still die if they are kept in a frozen storage environment for a long time.
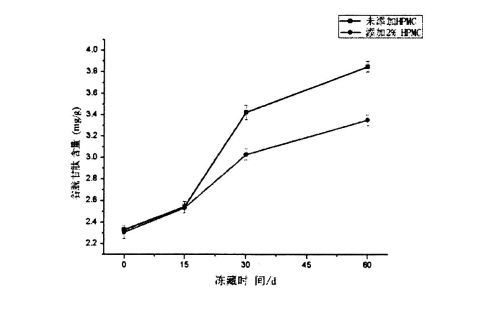
Seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 5.4, kandungan glutathione meningkat tanpa mengira sama ada HPMC ditambah atau tidak, dan tidak terdapat perbezaan yang signifikan antara jumlah tambahan yang berbeza. This may be because some of the active dry yeast used to make the dough have poor stress resistance and tolerance. Di bawah keadaan pembekuan suhu rendah, sel -sel mati, dan kemudian glutathione dibebaskan, yang hanya berkaitan dengan ciri -ciri ragi itu sendiri. It is related to the external environment, but has nothing to do with the amount of HPMC added. Therefore, the content of glutathione increased within 15 days of freezing and there was no significant difference between the two. However, with the further extension of the freezing time, the increase of glutathione content decreased with the increase of HPMC addition, and the glutathione content of the bacterial solution without HPMC was increased from 2.329a: 0.040mg/ g (frozen storage for 0 days) increased to 3.8514-0.051 mg/g (frozen storage for 60 days); while the yeast liquid added 2% HPMC, its glutathione content increased from 2.307+0 .058 mg/g (frozen storage for 0 days) rose to 3.351+0.051 mg/g (frozen storage for 60 days). This further indicated that HPMC could better protect yeast cells and reduce the death of yeast, thereby reducing the content of glutathione released to the outside of the cell. This is mainly because HPMC can reduce the number of ice crystals, thereby effectively reducing the stress of ice crystals to yeast and inhibiting the increase of extracellular release of glutathione.
5.4 Ringkasan Bab
Masa Post: Okt-08-2022